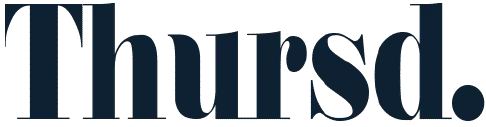Haven't yet heard about stomata and what this term means? Stomata are a vital part and component found in the pores of leaves, which are used to exchange gases in a plant.
Science and nature work in amazing ways, and stomata-breathing leaves have already made a humongous impression on botanists and plant fans. Keep reading to find a surprising video showing stomata breathing leaves in full spectrum.
What Are Stomata 'Breathing Leaves'?
Stomata are a scientific term used in the plant world to describe microscopic openings in the epidermis of plant leaves. Have you ever heard of it? If not, no worries, we're here to give you the 411 on stomata breathing leaves and everything you should know to understand fully.
Stomata, found in breathing leaves, are the specialized pores or openings present in the epidermis of the plant's cells. They play a crucial role in gaseous exchange during photosynthesis. What's the purpose of stomata in breathing leaves? We'll tell you below!
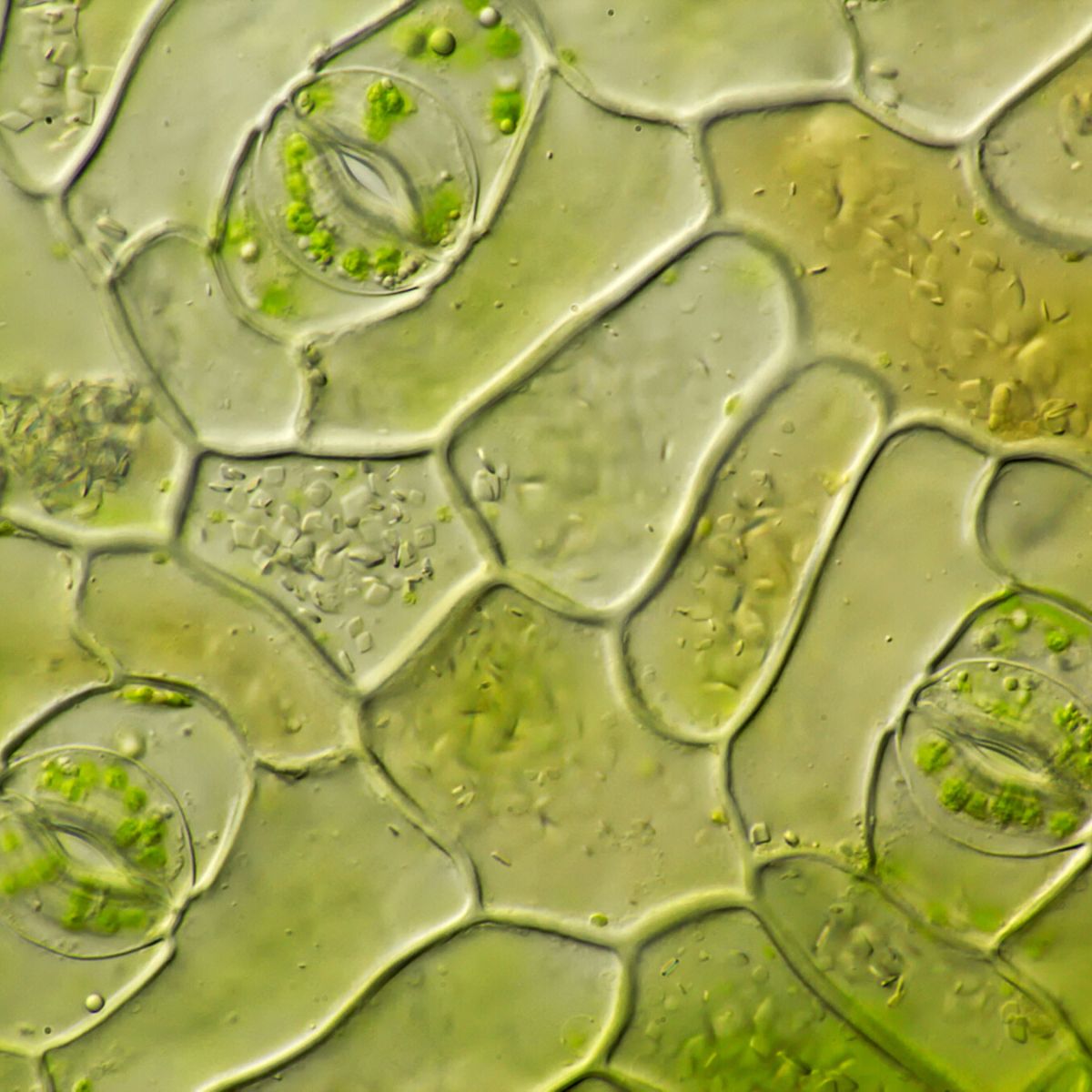
Photo found on Microscopy of Nature.
The Early Origin of Stomata Breathing Leaves
Unfolding the tale of our lush green planet brings us to one of the most pivotal actors in the story: stomata, the tiny pores nestled on the surface of leaves that have literally breathed life into our world. These inconspicuous cellular structures have been fostering the exchange of gases between plants and the atmosphere for over 400 million years, playing an indispensable role in the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems.
To understand the emergence of stomata, we delve into the prehistoric world, specifically the Silurian-Devonian period, when life started to make its remarkable shift from water to land. Amidst this great migration, early terrestrial plants faced a significant challenge: They had to devise ways of capturing sunlight and carbon dioxide (CO2) while preserving water, a resource now far less abundant than in their previous aquatic habitats. The answer, it seems, lies in the evolution of stomata.
Andrew Fleming, Professor of Plant Science at the University of Sheffield:
"Until now, the way plants form their intricate patterns of air channels has remained surprisingly mysterious to plant scientists."
According to Andrew and a group of researchers, the discovery of stomata breathing leaves, which is utterly a major one, shows that the movement of air through leaves shapes their internal workings – which has implications for the way we think about evolution in plants.
The earliest hint of stomata-like structures appears in the fossils of a primitive plant group called the 'rhyniophytes.' Found in the Rhynie chert, a Devonian fossil deposit in Scotland, these ancient plants exhibited rudimentary stomata on their stems. However, these stomata were non-functional and seemed to lack the dynamic opening and closing mechanism seen in modern plants.
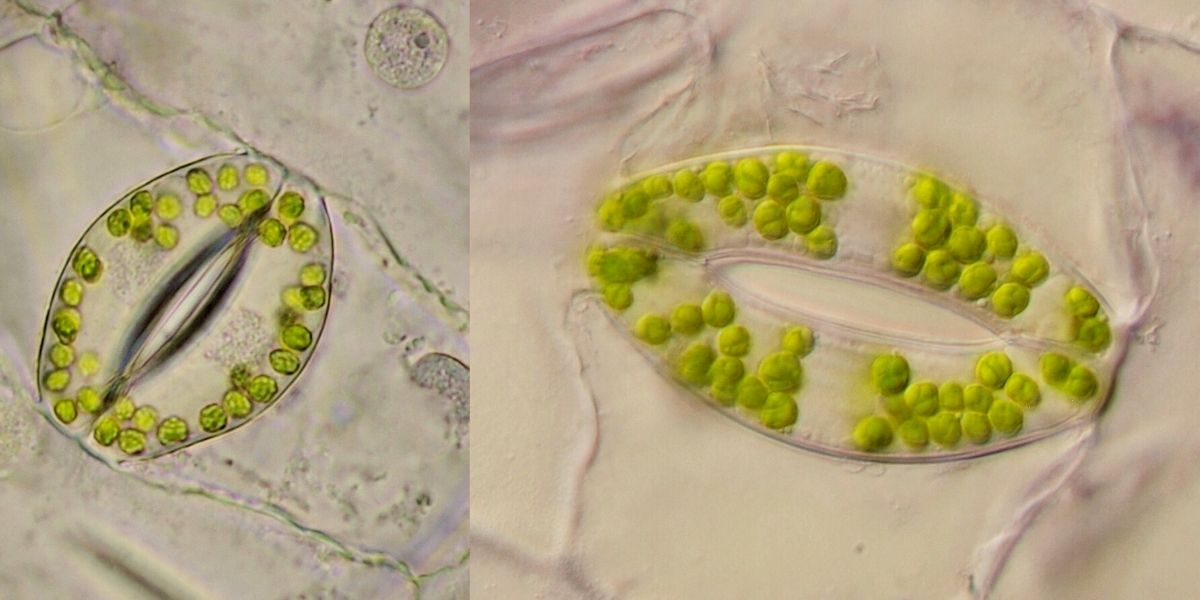
Photo found on Microscopy of Nature.
The Devonian Period
The evolution of active, 'breathing' stomata likely occurred later in the Devonian period, as evident in the fossils of early vascular plants like 'Zosterophyllum' and 'Baragwanathia.' The stomata in these plants not only featured guard cells but also were strategically positioned over air spaces, enabling the effective exchange of gases and transpiration - a precursor to the sophisticated system we observe today.
From an evolutionary perspective, the development of stomata represented a significant adaptive advantage. Plants with stomata could control their water loss while allowing the inflow of CO2 necessary for photosynthesis. Furthermore, the process of transpiration helped distribute water and nutrients throughout the plant, facilitating its growth and survival in diverse terrestrial habitats.
The elegant sophistication of stomatal design becomes clear when we consider their dynamic functionality. Governed by a mix of environmental cues and internal signals, the stomatal pores can open and close, modulating gas exchange in response to changing conditions. This remarkable flexibility has allowed plants to thrive even in environments of extreme aridity, heat, or cold.
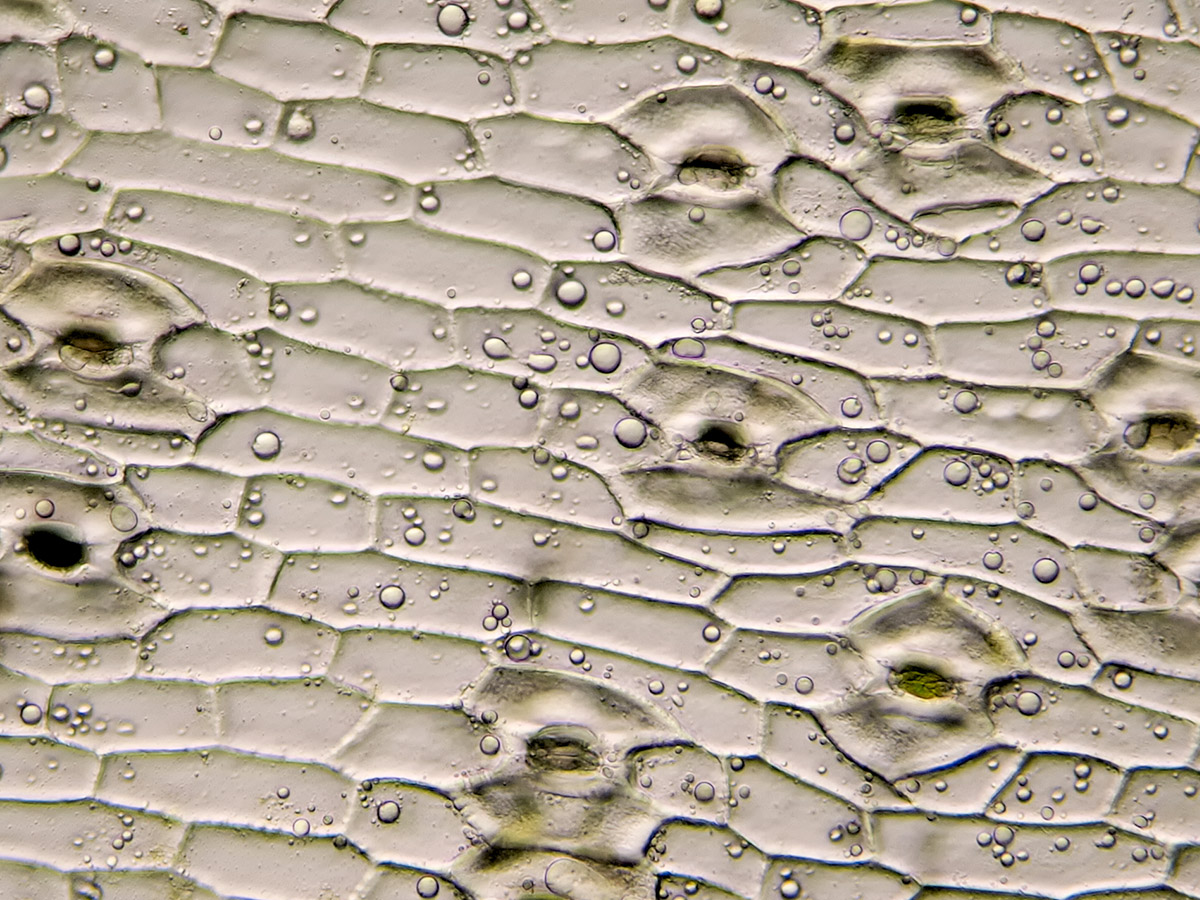
Photo found on Microscopy of Nature.
Incredible Ingenuity of Evolutionary Processes
In tracing the lineage of stomata, we get a glimpse of the incredible ingenuity of evolutionary processes. Over millions of years, these minute portals have optimized their function, aiding plants in colonizing virtually every corner of our planet. In doing so, they've not only transformed the Earth’s landscapes but have also dramatically influenced global climate patterns, shaping the biosphere as we know it.
Yet, as we confront the looming realities of climate change and environmental degradation, understanding the intricate workings of stomata becomes ever more crucial. It's a sobering reminder that our future may hinge, in part, on these tiny breathing pores of leaves, whose evolution started eons ago on the primeval landscapes of the Silurian-Devonian period.
As scientists deepen their exploration of stomatal function and evolution, one thing is certain - these remarkable breathing portals of leaves will continue to inspire and inform our strategies for sustaining life on our rapidly changing planet.
The most impressive part and results were shown through X-ray imaging to create a 3D model of a plant leaf’s cellular structure. The incredible study allowed plant scientists to show up close how the formation and placement of the stomata drive airflow to the cells.
Video Showing a Time-Lapse Capture of Stomata
This video shows a time-lapse capture of Tradescantia spathacea leaf stoma responding to transient changes in CO2 levels and relative humidity.
Video credits: Dr. Douglas Clark. (Footage received an Honorable Mention in Nikon's 2020 Small World in Motion Competition).
How Does Water Loss Happen Through Stomata?
Stomata make up only 3% of the leaf surface area, but most water loss happens through these openings due to the necessities of the photosynthesis gas exchange. Stomatal transpiration accounts for around 80 - 90% of plants' total water content changes. According to plant scientists, one of the most interesting processes to watch is the water leaving the stomata which are converted into water vapor taking the latent heat and causing the reduction in leaf temperature.
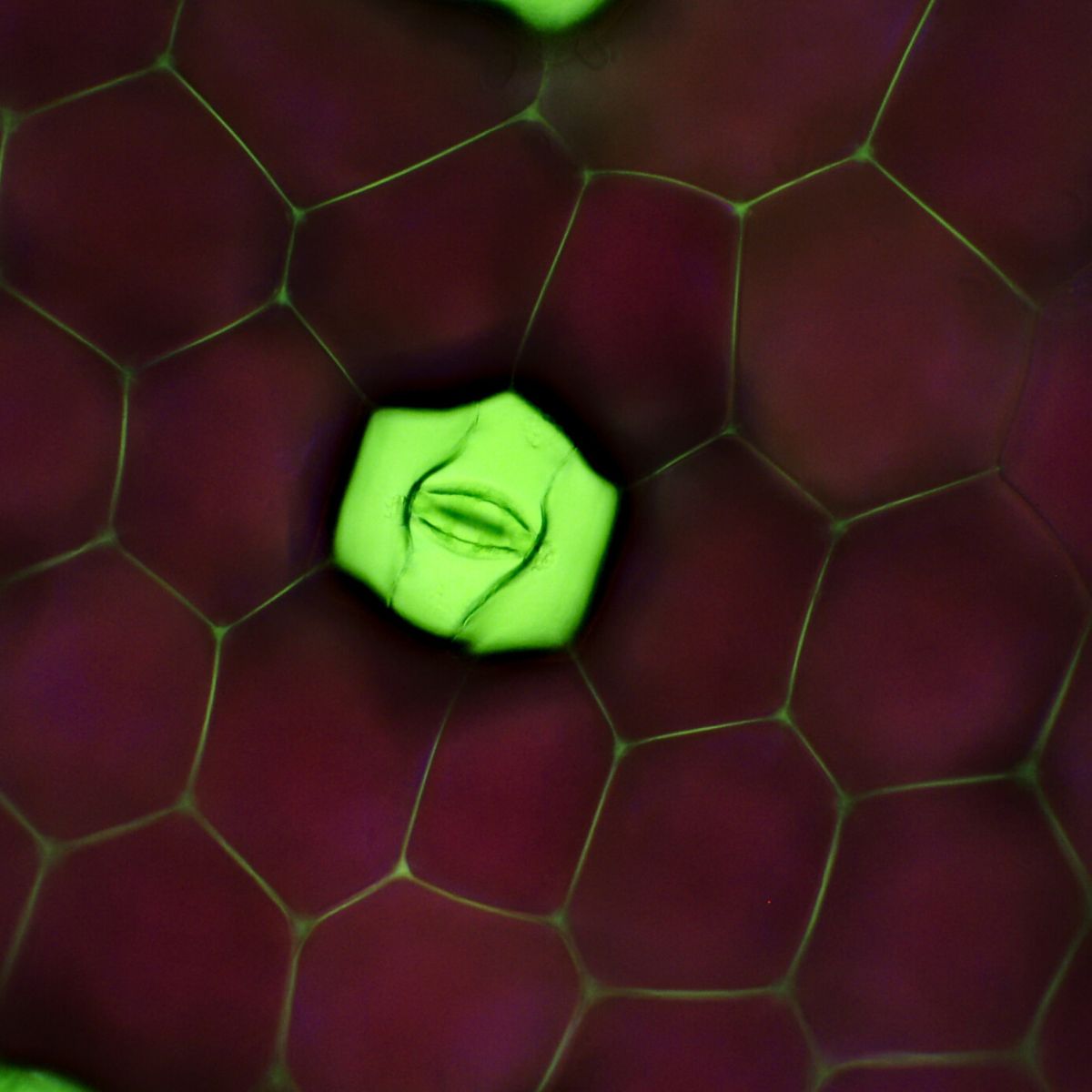

Photo found on Microscopy of Nature.
However, plants reduce stomatal openings during droughts to save water, thereby reducing CO2 exchange. When less water is available, dehydrated mesophyll cells release a phytohormone—abscisic acid—which causes the stomatal pores to close and reduce water loss.
Why Stomata Are Essential for Plant Life
Stomata may be tiny, but their role in plant life is massive. These microscopic pores are essential for gas exchange, enabling photosynthesis, regulating water loss, and helping plants adapt to their environment. Understanding how stomata function not only gives us deeper insight into plant biology but also highlights their impact on global ecosystems and climate regulation. Whether you're studying plant science or simply curious about how leaves "breathe," stomata offer a fascinating look into the hidden mechanics of nature.
Header image by @sciencephotolibrary