World Seagrass Day, on March 1st, is a United Nations-designated event to raise awareness about the vital role seagrass ecosystems play in marine environments and climate regulation. Established in May 2022, this day emphasizes the urgent need for conservation actions to protect and restore seagrass habitats. Seagrasses evolved from terrestrial plants, which recolonised the ocean 70 to 100 million years ago.
More Knowledge About Seagrass on World Seagrass Day
Seagrasses are unique flowering plants that thrive beneath the surface of shallow coastal waters, where they form vast underwater meadows. Despite their inconspicuous presence, these aquatic plants play an indispensable role in maintaining the health of the world’s oceans. There are around 60 known species of seagrasses, spread across four main families: Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae, and Cymodoceaceae. Together, these species cover the coastlines of 159 countries across six continents, occupying an estimated 300,000 square kilometers of seabed.
What makes seagrass truly remarkable is its immense ecological value. A single acre of seagrass can support close to 40,000 fish and as many as 50 million small invertebrates, offering shelter, food, and nursery grounds for a wide array of marine life. These meadows are biodiversity hotspots, contributing directly to the health of fisheries and the overall balance of coastal ecosystems.
Seagrass also plays a vital role in mitigating climate change through its incredible carbon-storing capacity. Although these meadows cover only about 0.1% of the ocean floor, they account for roughly 10 to 18% of all carbon captured and stored by the ocean, a process known as blue carbon sequestration. Globally, it’s estimated that seagrasses have stored nearly 20 billion tons of carbon over time, capturing it up to 35 times faster than tropical rainforests.
In addition to its role in carbon storage, seagrass meadows are exceptional oxygen producers. Just one hectare of healthy seagrass can generate around 100,000 liters of oxygen per day, enriching coastal waters and supporting countless species that depend on oxygen-rich habitats. At the same time, the dense root systems of seagrasses help stabilize seabeds, reducing erosion and protecting coastlines from wave action and storm surges — buffering communities against the impacts of rising seas and increasingly extreme weather events.
Seagrasses reproduce both sexually and asexually. They flower and produce seeds, but they also spread through underground rhizomes, enabling them to form extensive meadows over time. However, these valuable ecosystems are disappearing at an alarming rate. Human activities such as coastal development, pollution, destructive fishing practices, and climate change contribute to the loss of seagrass meadows — currently, they are being destroyed at an estimated rate of three square meters every second.
Seagrass's fate is directly tied to the health of our oceans and the stability of our climate. By understanding the extraordinary services these humble underwater plants provide, from supporting marine biodiversity to storing vast amounts of carbon, we can better appreciate the urgent need to protect and restore them. Seagrass might not always be visible, but beneath the waves, it’s working tirelessly for the planet.
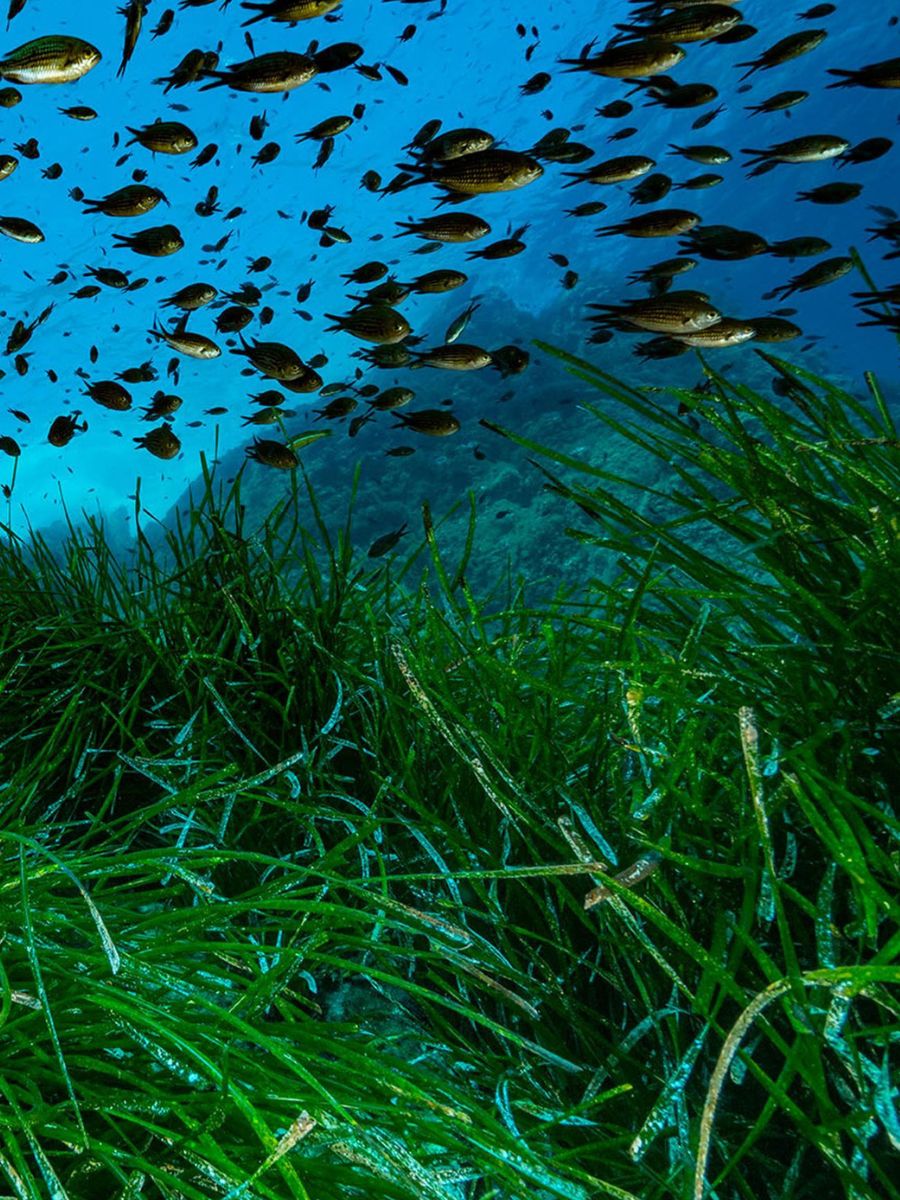

Threats to Seagrass Habitats
World Seagrass Day calls for awareness. Despite their importance, seagrass ecosystems face numerous threats:
Pollution: Runoff containing fertilizers, pesticides, and other pollutants can degrade water quality, adversely affecting seagrass health.
Physical Disturbance: Activities such as dredging, anchoring, and coastal development can physically damage seagrass beds, leading to habitat loss.
Climate Change: Rising sea temperatures and increased frequency of marine heatwaves can cause seagrass die-offs and hinder their capacity for carbon sequestration.
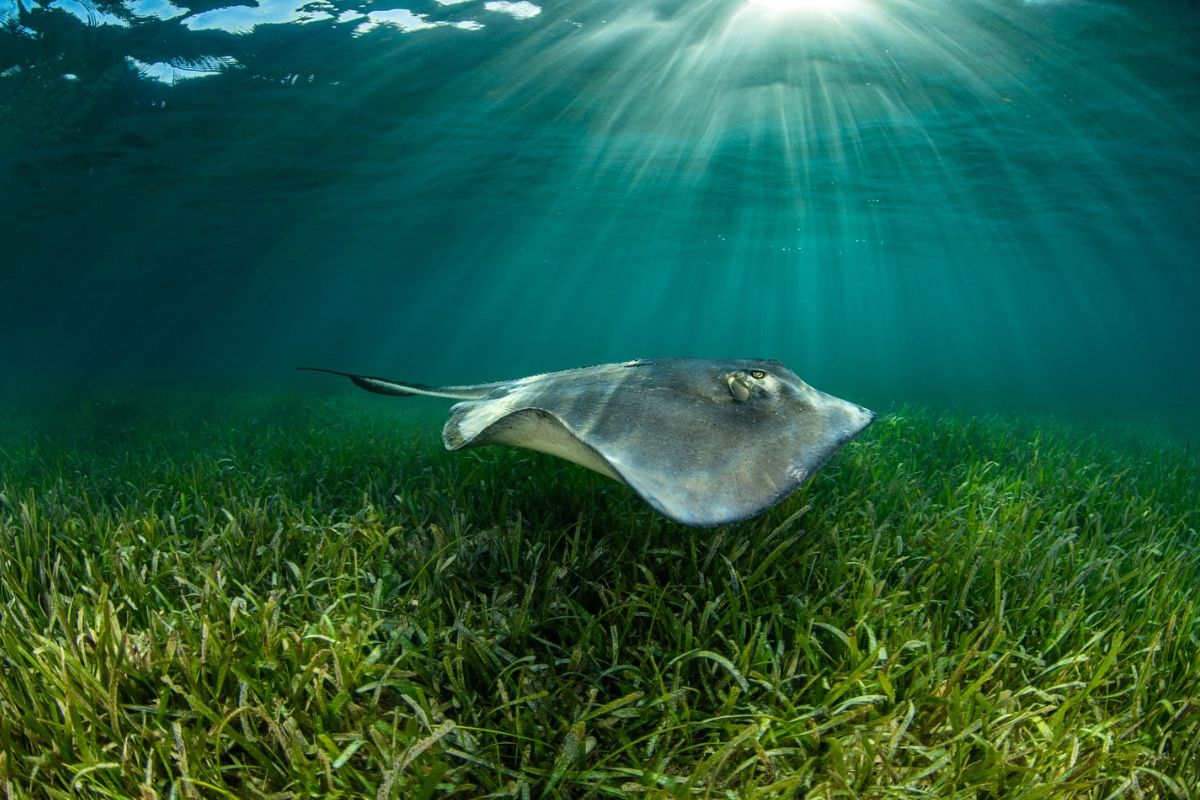

Conservation and Restoration Efforts
Recognizing the critical role of seagrasses, various conservation and restoration initiatives have been implemented:
Protected Areas: Establishing marine protected areas helps safeguard seagrass habitats from destructive activities.
Restoration Projects: Efforts to replant and restore degraded seagrass meadows are underway in many regions, aiming to enhance biodiversity and carbon storage capacities.
Policy Measures: International agreements and national policies are increasingly focusing on the protection of seagrass ecosystems as part of broader climate change mitigation and marine conservation strategies.

How You Can Help
On this celebration of World Seagrass Day, individuals can contribute to seagrass conservation through various actions:
Reduce Pollution: Minimize the use of fertilizers and pesticides, and properly dispose of waste to prevent runoff into coastal waters.
Support Sustainable Practices: Choose seafood from sources that employ sustainable fishing methods, reducing impacts on seagrass habitats.

Participate in Local Conservation Efforts: Engage with organizations dedicated to protecting and restoring seagrass meadows through volunteer opportunities or advocacy.
By understanding and valuing the essential services provided by seagrass ecosystems, we can take informed actions to ensure their preservation for future generations.
Header Picture @carltonward