Sustainable floriculture represents an important bridge between commercial flower production and environmental management, and its thoughtful implementation means flower cultivation practices significantly contribute to preserving the environment and the planet by extension. The demand for flowers continues to grow, and so does the need for sustainable practices to prevent environmental degradation, more so, biodiversity conservation, while maintaining economic viability. More simply stated, the flower industry's sustainability depends on recognizing and enhancing the symbiotic relationship between floriculture industry operations and the broader ecosystem, particularly through habitat protection and pollinator support strategies.
The Importance of Biodiversity in Sustainable Floriculture
Biodiversity is critical for the resilience of ecosystems and agricultural systems. In floriculture, diverse plant species contribute to the health of the soil, the cycling of nutrients, and the stability of the ecosystem. A diverse ecosystem of flowers and plants can help mitigate the impacts of pests and diseases, reducing the need for extensive chemical interventions that can harm the environment. Moreover, a higher level of biodiversity enhances pollination efficiency, which is essential for the reproductive success of flowering plants.
Sustainable floriculture practices are vital for maintaining biodiversity, as they can help prevent the negative consequences of monoculture—the cultivation of a single crop species over an extensive area. Monoculture can lead to a reduction in genetic diversity and make ecosystems more vulnerable to fluctuations. Implementing sustainable practices in floriculture can contribute to the preservation of native plant species, the restoration of degraded ecosystems, and the promotion of ecological balance.
Through the cultivation and conservation of diverse flowering plants, the industry contributes significantly to the preservation of plant species and their habitats. As a branch of horticultural science, floriculture's focus on growing and marketing ornamental plants can be oriented toward sustainability through practices that reduce environmental degradation, maintain productivity, build economic viability, conserve resources, and support stable communities.

In agroecosystems, biodiversity performs numerous ecological services other than mere production, including nutrient recycling, microclimate regulation, hydrological process management, suppression of undesirable organisms, and detoxification of harmful chemicals. These services form the foundation of sustainable floriculture operations, which, when approached with ecological principles in mind, means that floriculture becomes a driver of biodiversity enhancement rather than depletion.
The sustainability of floriculture operations centers on implementing practices that maintain environmental integrity while ensuring economic viability. This includes integrated nutrient management (INM), integrated pest management (IPM), crop rotation, and efficient water utilization, all of which are approaches that minimize environmental impacts while supporting the diverse biological communities that underpin healthy ecosystems.

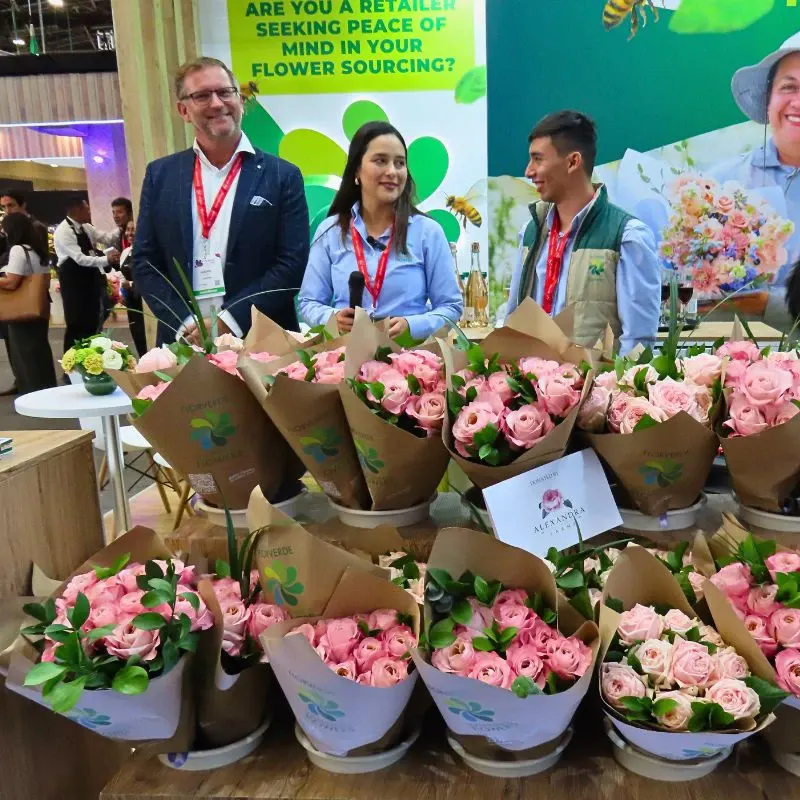
Florverde Sustainable Flowers (FSF) farms, for instance, actively preserve ecosystems around them and protect native species. The floriculture sector in the South American region, according to Daniela España of FSF, is committed to pollinator conservation, integrating IPM practices that reduce pesticide use and promote pollinator-friendly environments. The protection of wetlands and natural reserves within farms also provides critical habitats for more than 170 bird species, including the Tingua Moteada, a conservation priority in Colombia.
Habitat Protection Strategies in Sustainable Floriculture
One of the most effective ways to conserve biodiversity in floriculture is through habitat protection. This represents a fundamental approach to biodiversity conservation within floriculture operations. It can be achieved by creating designated conservation areas where native flora and fauna can thrive without the pressures of agricultural development.
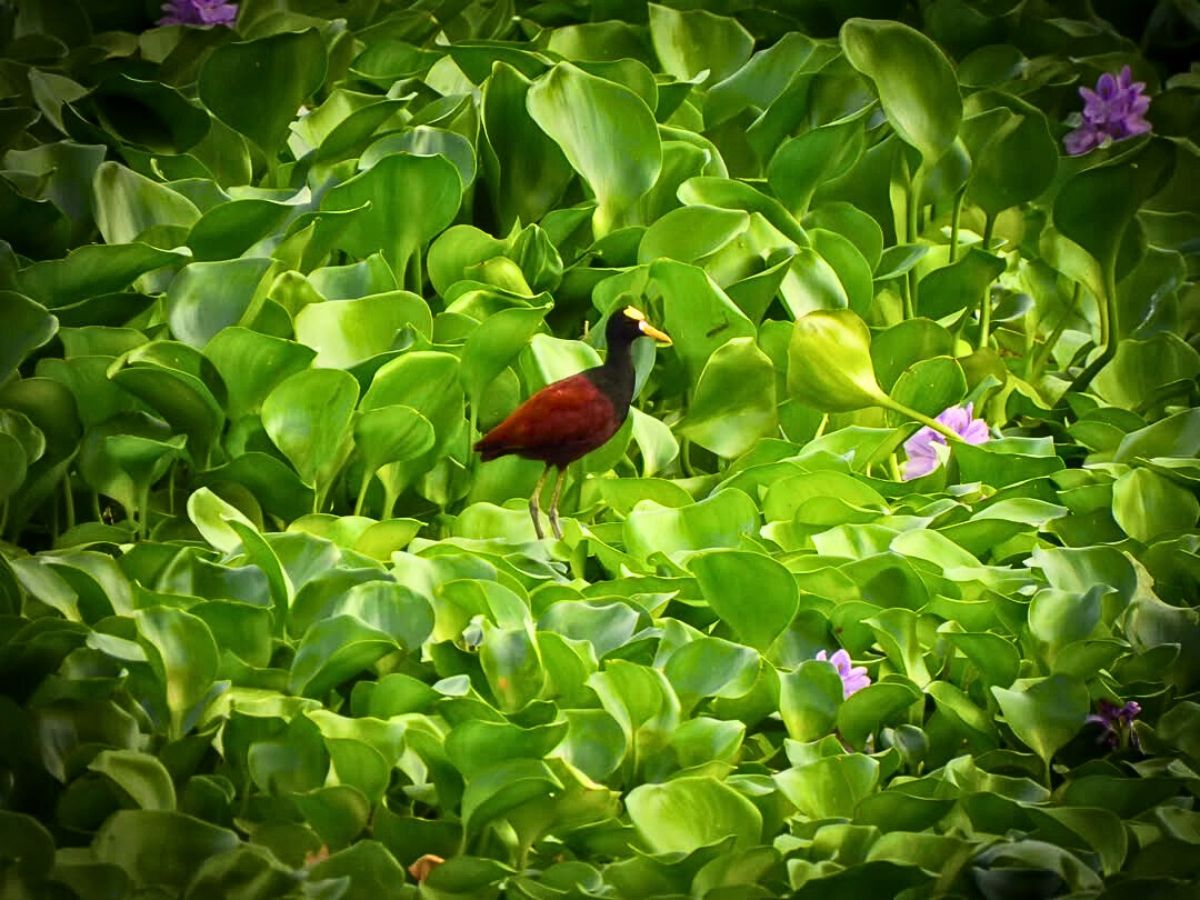

The establishment of protected areas provides crucial safeguards for threatened species, but these measures must be complemented with species-specific conservation actions to ensure their long-term persistence. Ecological restoration complements, not substitutes for, conservation efforts, requiring careful balance in resource allocation between these complementary approaches.
Habitat protection involves practices such as preserving natural landscapes, in which case floriculture facilities can reduce land clearing and preserve surrounding natural habitats, which serve as vital ecosystems for native wildlife, including pollinators and other beneficial organisms. It also involves implementing buffer zones around areas of cultivation, which means growers can reduce pesticide runoff and enhance habitat diversity. Buffer zones may consist of native plantings that attract beneficial insects and birds.

Initiatives to restore degraded habitats can likewise enhance biodiversity and create new habitats for wildlife. For instance, floriculture operations can engage in rewilding efforts that involve planting native species in previously cleared areas. Also, incorporating agroforestry and the integration of trees and shrubs into floriculture operations not only provides shade and improves soil health but also supports biodiversity. The combined habitats nurture a variety of species, creating a more robust ecological environment.
Another essential component of habitat protection involves the collection and conservation of native seeds. Collaborative projects like the Queensland Seeds for Life Project show how botanical institutions can work together to enhance plant biodiversity conservation through seed collection and long-term storage. These initiatives prioritize species of conservation concern, with collected seeds supporting scientific research and utilization programs that advance sustainable floriculture practices.

Plus, establishing perennial floral plantings in unused margins of agricultural fields represents another effective habitat protection strategy. Such dedicated areas can significantly support beneficial insects, including both pollinators and arthropod predators, even within conventional commercial farming operations. These habitat enhancements create ecological stepping stones within fragmented landscapes, allowing species to move between larger habitat patches and maintaining genetic connectivity among populations.
Pollinator Diversity Support - An Essential for Sustainable Floriculture
Wild pollinators—primarily insects that facilitate plant reproduction—are essential components of ecosystems and food systems globally. Contrary to common perception, wild pollinators, not honey bees, provide the majority of pollination services worldwide. An estimated three-quarters of the world's most important food crops and 87% of all flowering plants depend on pollinator contributions, making them indispensable for both human and environmental well-being.
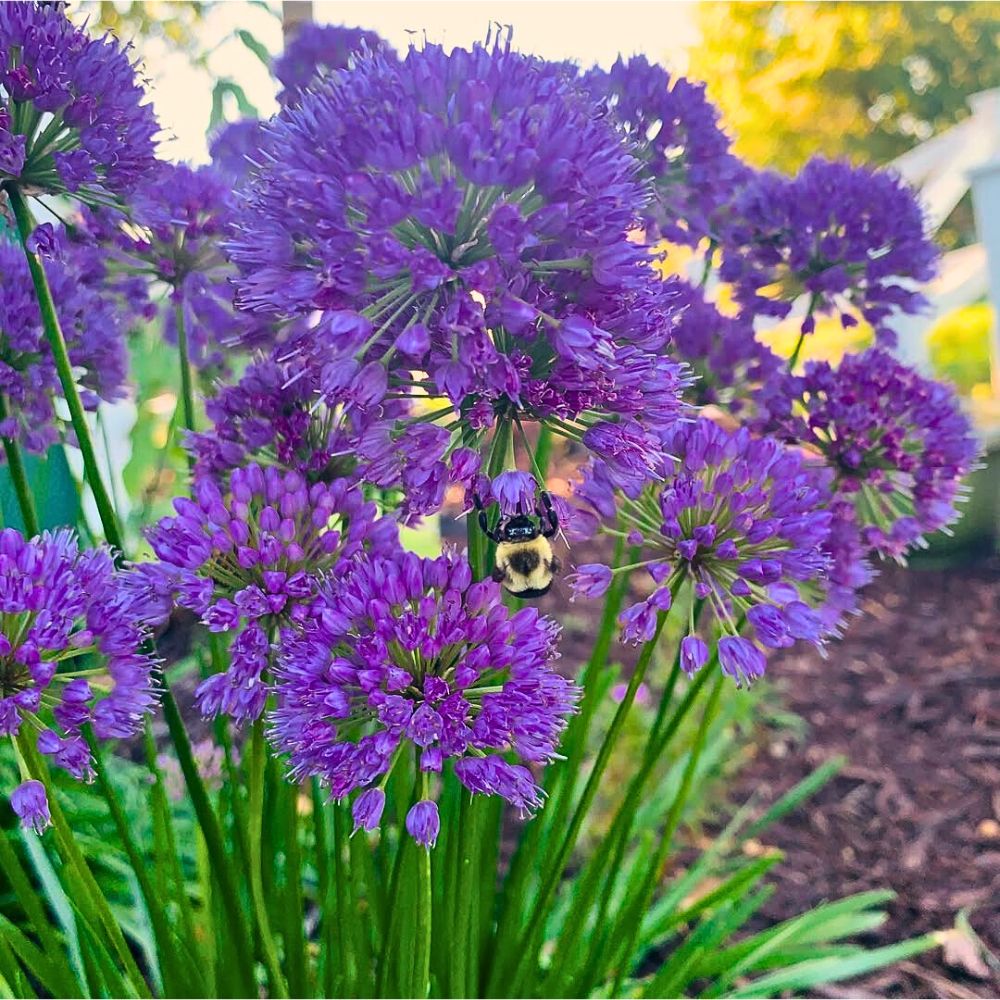

Research has demonstrated that even small-scale flower plantings within agricultural landscapes can significantly increase pollinator abundance and wild bee diversity. These planted areas support not only common pollinators but also specialists that may be more vulnerable to habitat loss. The diversity of pollinator communities improves their resilience to environmental changes and stochastic events, contributing to more stable ecosystems and consistent pollination services.
Innovative Approaches to Pollinator Conservation
Without a doubt, pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds play a crucial role in the reproductive success of flowering plants. In floriculture, supporting pollinator populations is essential for both ecological health and crop yields. To promote pollinator health, floriculture operations can undertake several initiatives. Planting pollinator-friendly species and incorporating a variety of flowering plants that bloom at different times during the growing season can provide a continuous food source for pollinators. Native and locally adapted plants, for instance, encourage the attraction of native pollinator species, which are often more effective than non-native ones.

Additionally, providing nesting support for pollinators using local or waste materials like hollow stumps, packed bare soil, or old wood with boreholes enhances habitat value beyond just floral resources. This comprehensive approach addresses multiple aspects of pollinator life cycles, supporting more robust and diverse pollinator communities.
Minimizing pesticide application is also key to protecting pollinator health. Growers and floriculturists can adopt IPM approaches that deploy biological controls, mechanical controls, and other nonchemical methods, thereby reducing reliance on chemical pesticides. Floriculture operations can also create nesting opportunities for pollinators. For example, leaving patches of bare ground can provide nesting sites for ground-nesting bees, while planting specific shrubs can support butterflies and other pollinator species.

There are also innovative approaches to pollinator conservation. Such include the Farming with Alternative Pollinators (FAP) methodology which offers an innovative approach to supporting pollinators while maintaining economic viability. Rather than dedicating land solely to wildflowers, which farmers might view as weeds occupying valuable acreage, FAP recommends allocating approximately 25% of field space as ‘pollinator habitat enhancement zones’. These areas are planted with marketable species—such as oilseeds, spices, vegetables, or medicinal plants—that simultaneously attract pollinators and generate revenue.
Furthermore, educating the community about the importance of pollinators and encouraging local gardening practices that support them can enhance biodiversity even beyond the floriculture industry and its operations. Collaborative efforts with local schools, communities, and organizations can nurture a culture of biodiversity conservation.

Integrated Conservation Approaches for Maximum Impact
Effective biodiversity conservation in floriculture requires integrated action addressing multiple ecosystem aspects simultaneously. This integrated approach combines habitat protection, pollinator support, sustainable cultivation practices, and economic considerations. Studies show that ecological intensification—managing agricultural production by supporting existing ecosystem processes—can reduce pollinator decline while benefiting agricultural production.
When plant cultivation helps pollinators, pollinators help in plant/crop cultivation. Research reviews analyzing hundreds of studies have confirmed that supporting pollinators through ecological intensification practices yields mutual benefits for both conservation and production. Pollinators provide services valued at several billion dollars annually, supporting not just floricultural production but entire biological communities.

Future Directions for Biodiversity-Friendly Floriculture
The path forward for biodiversity-friendly, sustainable floriculture requires continued research, education, and collaboration among growers, researchers, policymakers, and consumers. Addressing implementation barriers while highlighting biodiversity conservation's economic and ecological benefits will enhance and accelerate the flower industry's transition toward sustainability.
Small-scale flower plantings have proven effective for enhancing pollinator communities, suggesting that even modest conservation efforts can benefit significantly. Focusing on these achievable interventions may, therefore, provide an accessible entry point for flower operations beginning their floriculture sustainability journeys.
Featured and header image by @flowersofcolombia.