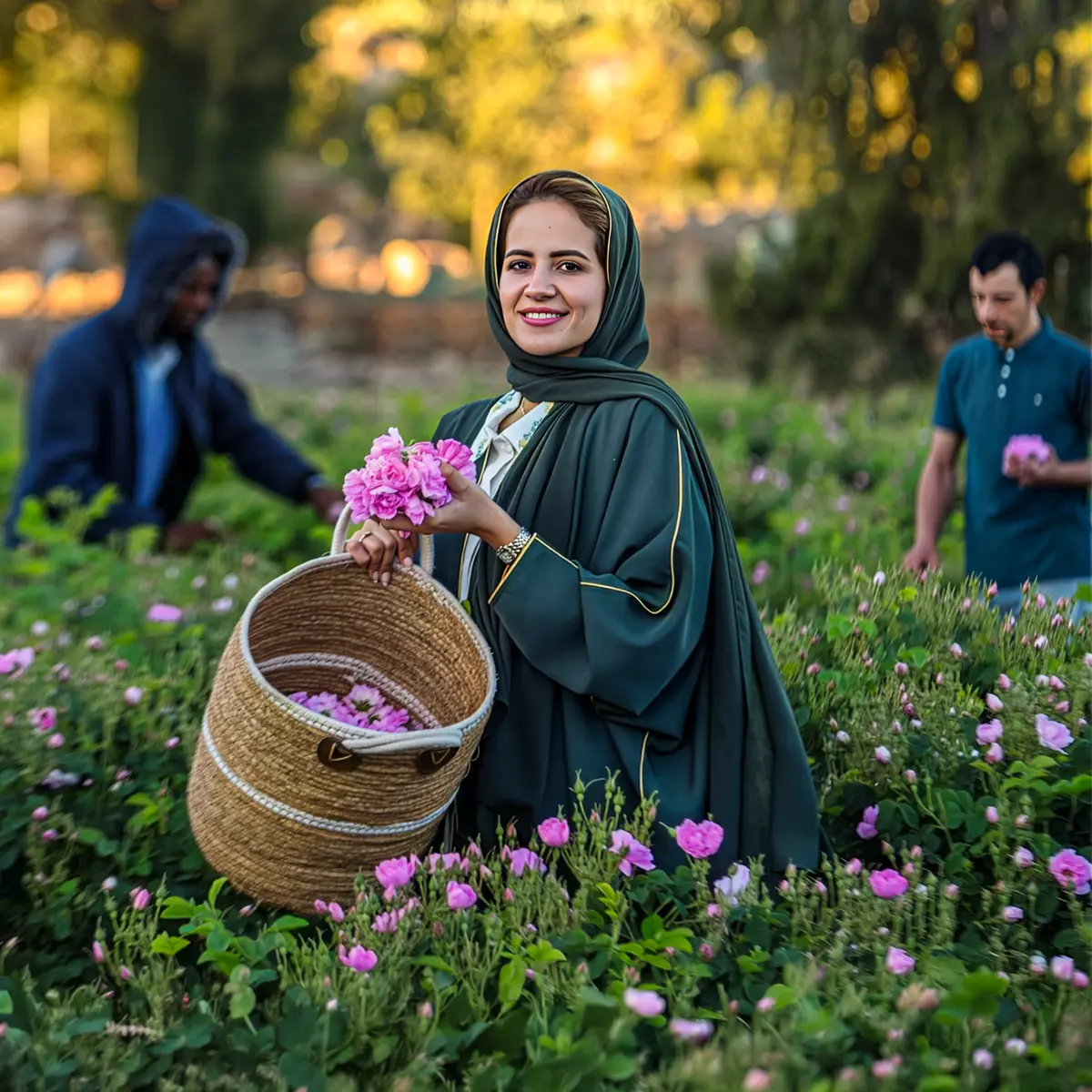
One of the most important dates for the flower business is Valentine’s Day, and without a doubt, the protagonists of this date are the flowers, mainly (red) roses. For flower growers, Valentine's Day is not just a date on the calendar; it's a season of love that requires meticulous planning and preparation.
Cupid's first visit is to nurseries around the world, ensuring flowers will be at their best for V-Day. So, as this little angel's arrows start to fly, let's take a closer look at how flower growers can optimize their Valentine's Day production and sales for a blooming success.
Valentine's Day in the Eyes of the Grower
Valentine's Day is not just a celebration for lovers around the world. It's so much more. It's a feast for the whole floriculture industry, and everyone's invited. Also, for the grower, with whom the celebration starts long before that one fine day in February. This is Valentine's Day from the perspective of the flower producer.
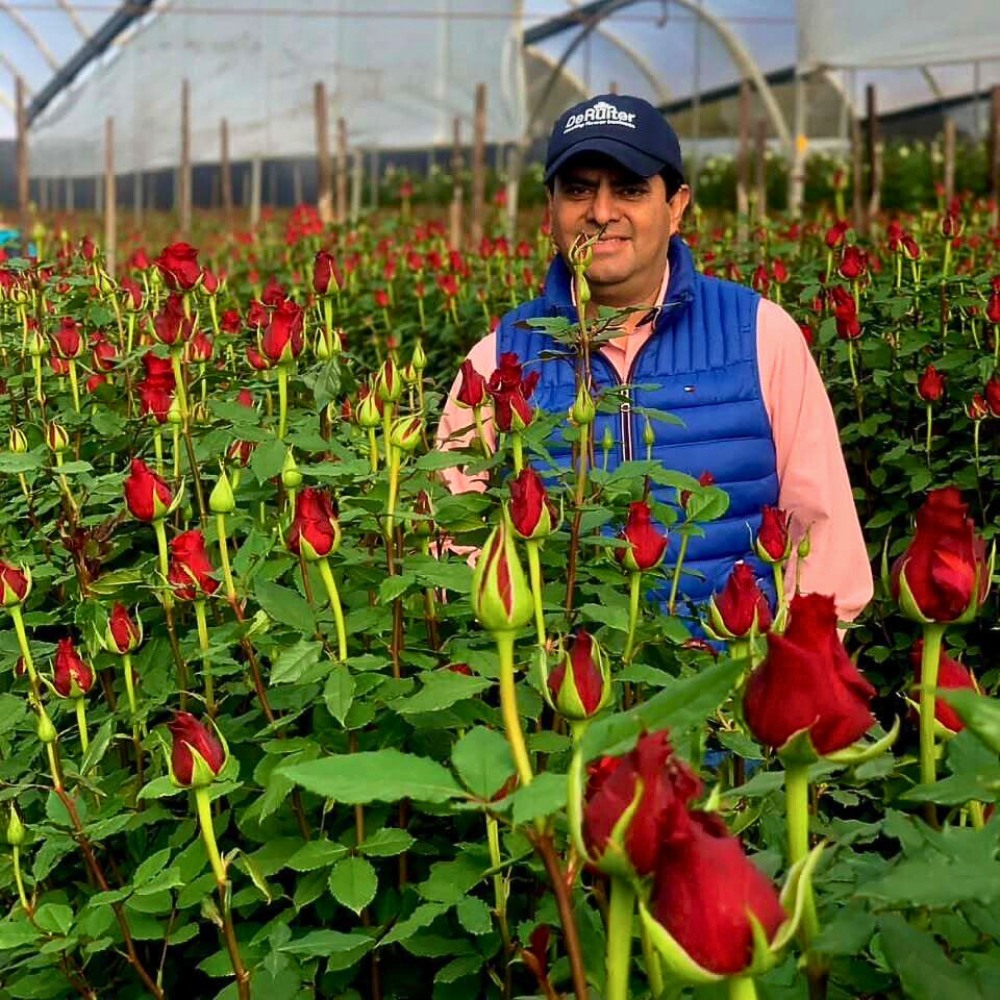

1. Start on Time
Valentine's Day might be in mid-February, but the groundwork starts months in advance. Successful growers begin planning and planting well ahead of time. By selecting the right varieties, timing the planting schedule, and ensuring optimal growing conditions, they can ensure a bountiful harvest when the big day arrives.
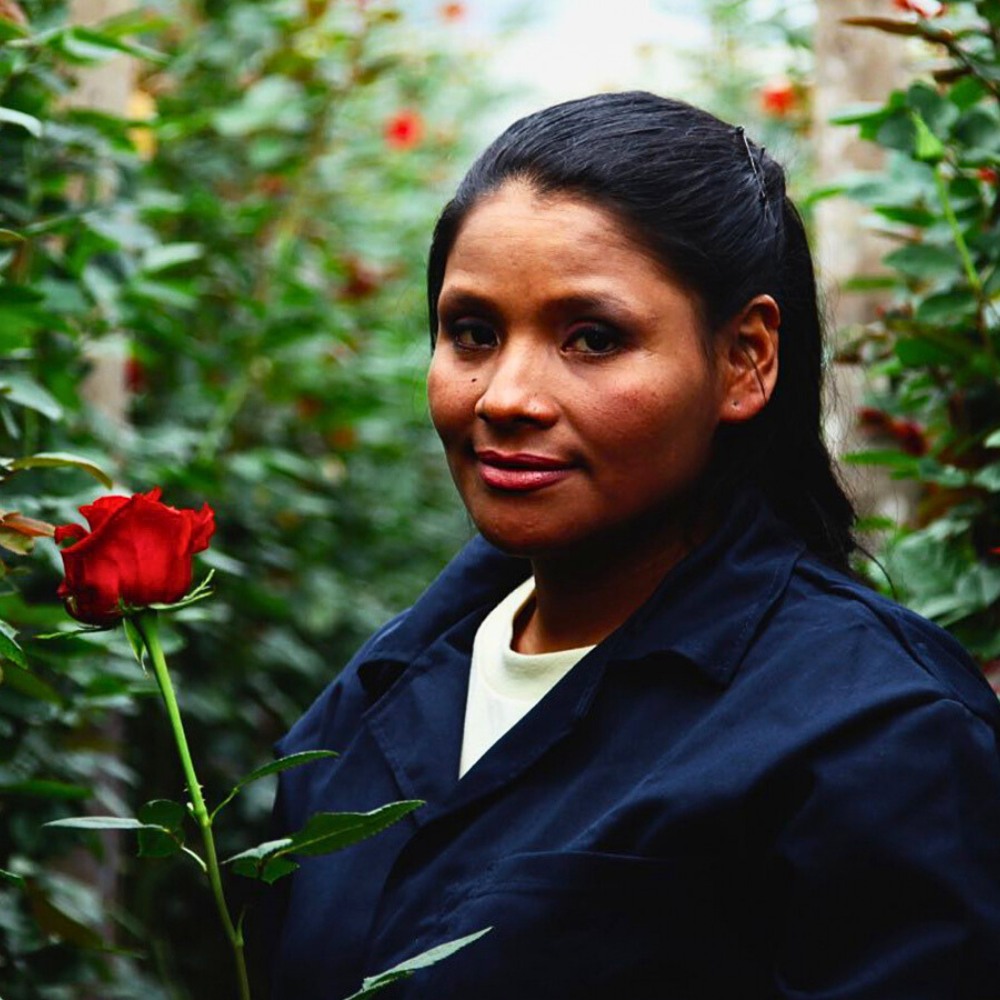

Grower Rosaprima from Ecuador says:
"When preparing for busy holidays, our process remains the same. It involves hands-on development and inspection by expert eyes. Four months before, we know which varieties will be in high demand and ensure all our areas are in check."

Bart Engels from Kenyan nursery Red Lands Roses explains how they step-by-step prep up for V-Day already around August:
"Valentine’s Day is a key peak period for Red Lands Roses, driving a significant spike in demand for premium roses and contributing substantially to revenue. Ensuring top quality, reliability, and timely deliveries is crucial for maintaining strong customer relationships.
Production preparation begins six months in advance with crop planning to optimize pruning cycles. Three to four months prior, the focus shifts to monitoring growth cycles, targeted nutrition, and pest control. In the final one to two months, quality control measures are reinforced, and operational teams are trained to handle high volumes efficiently."
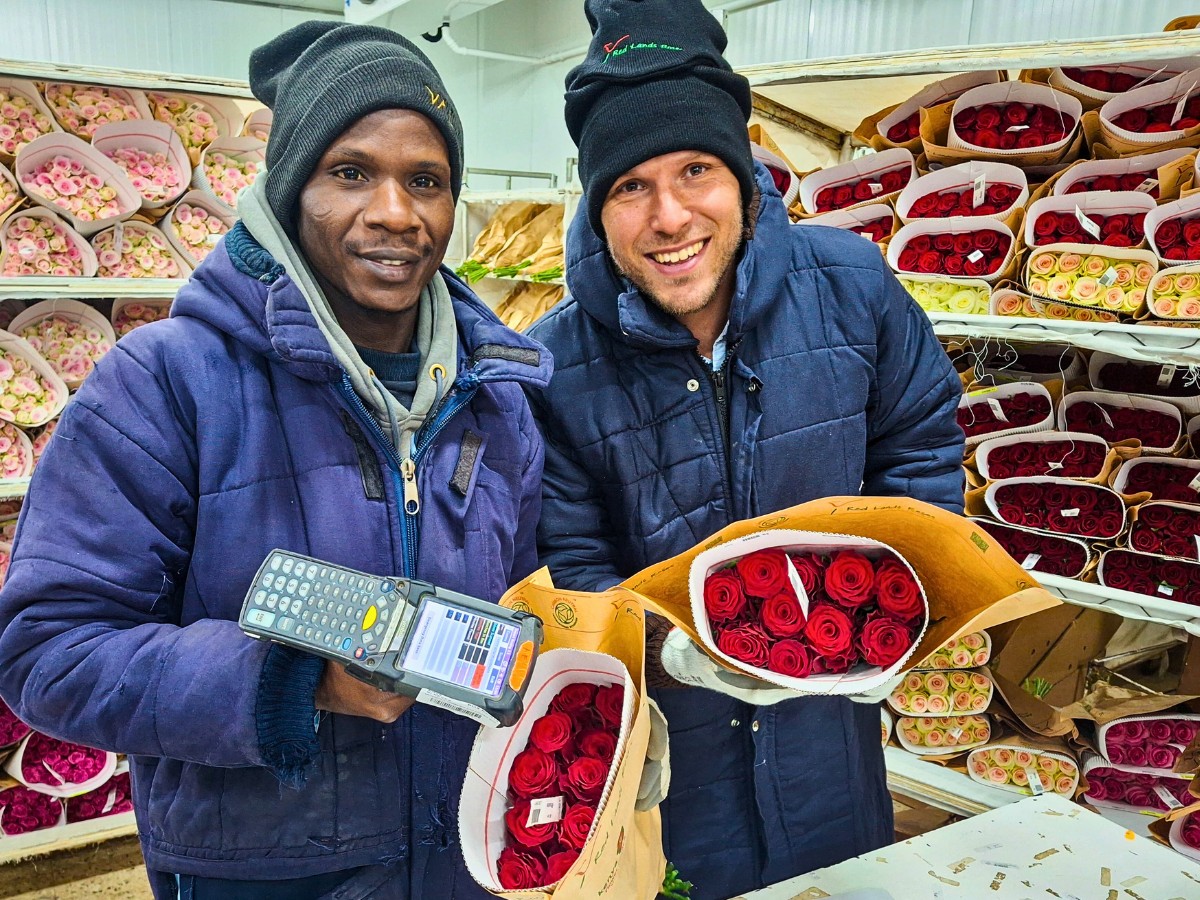

Bart adds:
"Sales preparation starts in October-November with customer engagement to forecast demand and secure pre-orders. In December and early January, sales and logistics planning ensure smooth order allocations and shipments. From January to February, close coordination between production, post-harvest, and commercial teams guarantees timely deliveries.
Our top varieties will likely be premium red roses and pink spray roses, with Rose Rhodos, Spray Rose Giselle, and Spray Rose Bal Musette expected to be bestsellers due to their rich color, long vase life, and strong stems. Growing demand for white and pastel shades may also drive diversification."
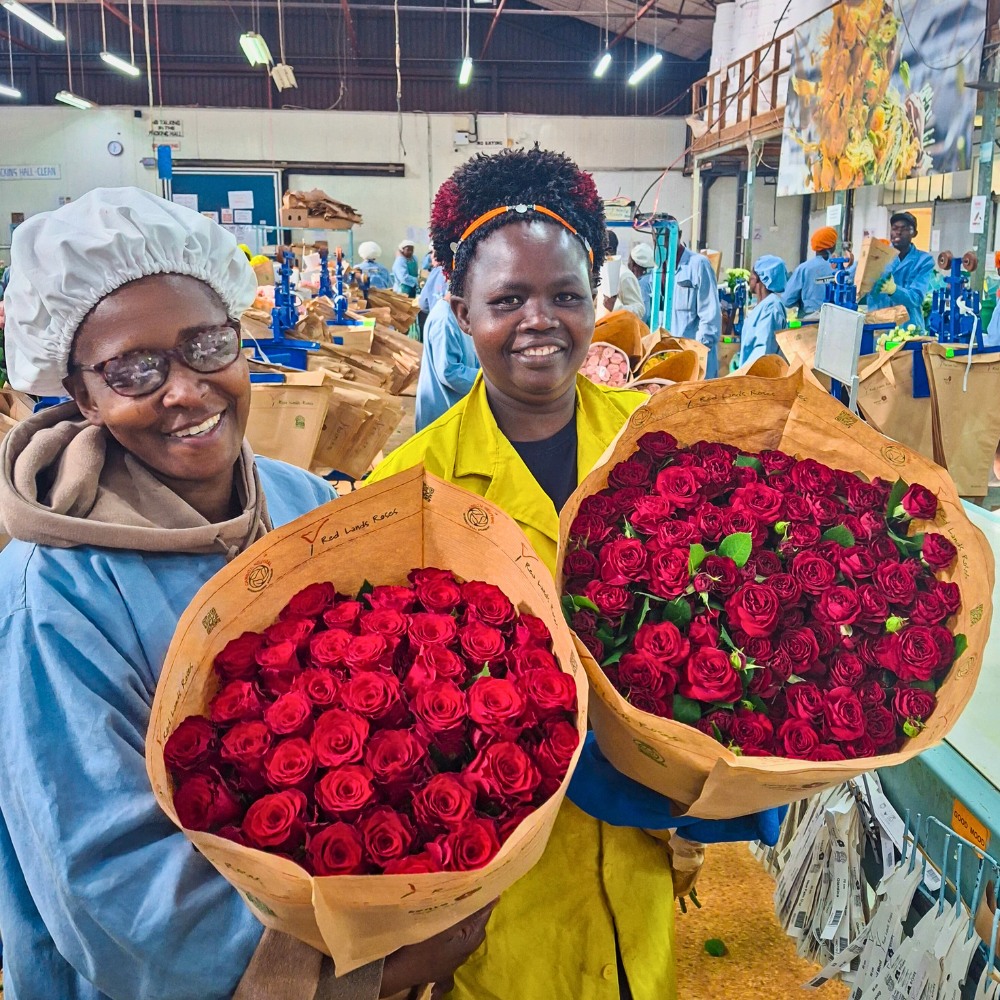

Variety is the spice of life, and it applies to the floral world, too. Offering a diverse range of flowers, from classic red roses to unique and trendy varieties, can attract a broader customer base. Experiment with different colors and shapes to create captivating and eye-catching bouquets.
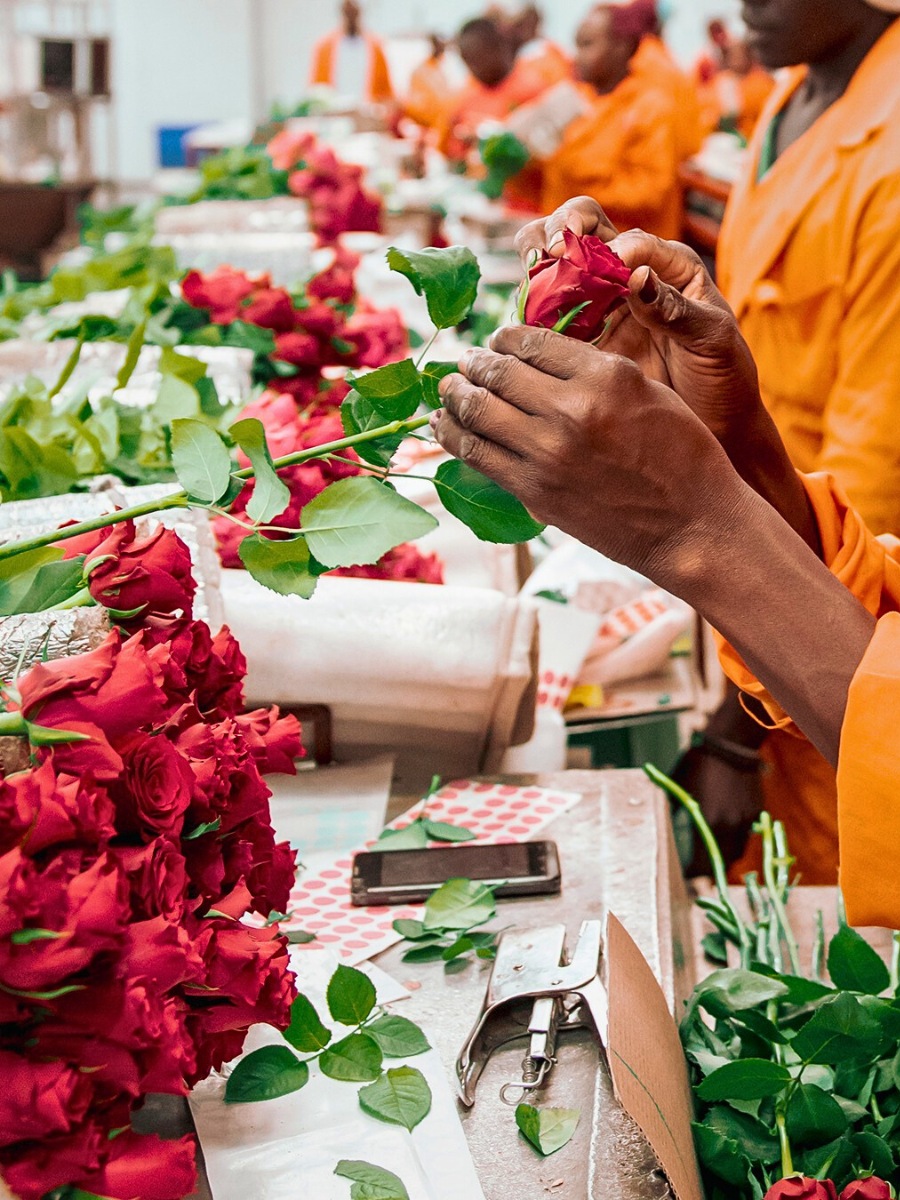

2. Quality First!
Quality is key when it comes to Valentine's Day. Focus on nurturing healthy, vibrant flowers. Proper care, nutrition, and pest control are essential to ensure that your blooms meet the highest standards. Quality blooms not only look better but also have a longer vase life, which keeps customers satisfied. A good customer is not just the one who buys your flowers, but also the one who returns to you to buy again and again.
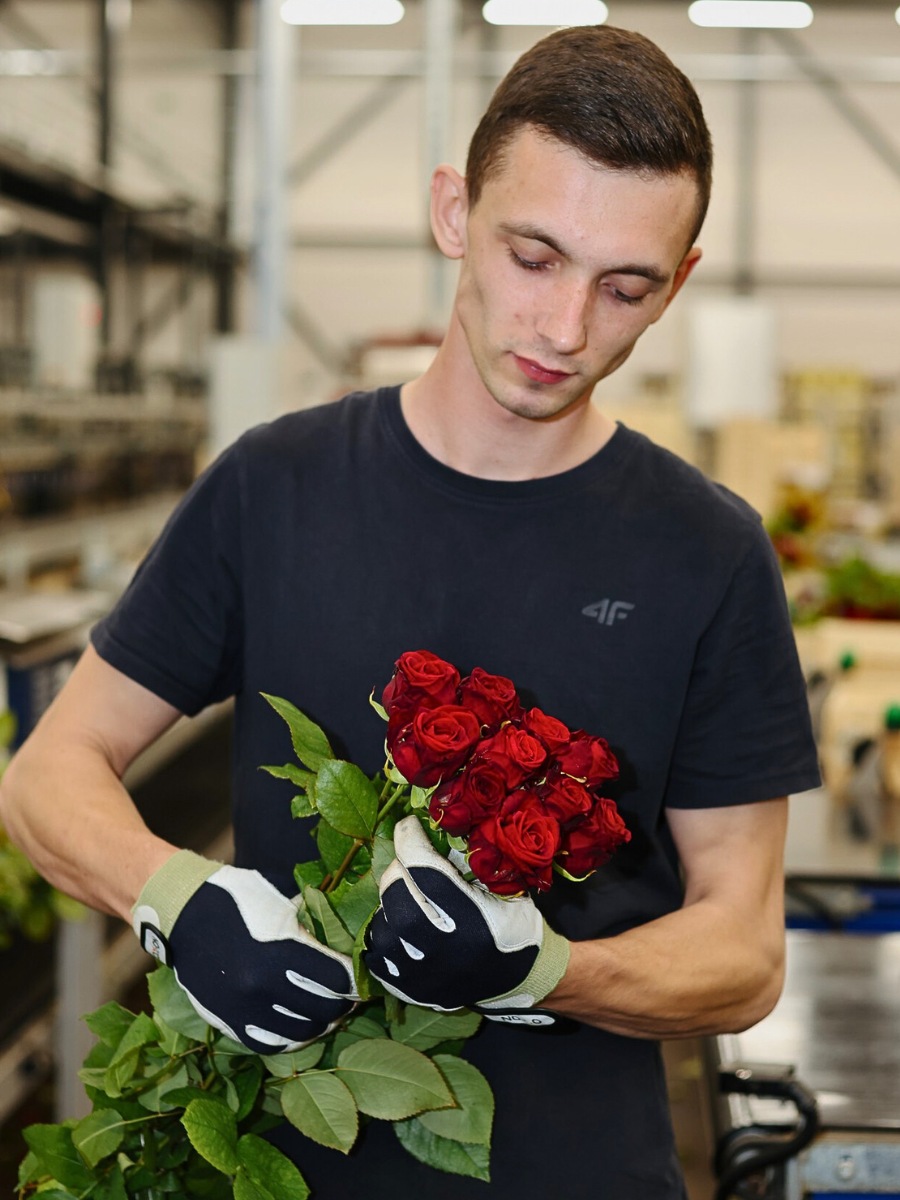

Efficiency is crucial during the Valentine's Day rush. Plan your harvest carefully to ensure that you have enough flowers at their peak of freshness. Swift post-harvest handling, including proper hydration and temperature control, will help preserve the quality of your blooms.
The presentation can make or break a sale. Invest in eye-catching and eco-friendly packaging that complements your blooms. Thoughtfully designed packaging can enhance the perceived value of your flowers and set you apart from the competition.

3. Sell Well
Consider offering pre-sell and pre-order options to customers. This not only helps you gauge demand but also reduces last-minute rush and stress. Customers appreciate the convenience of planning and knowing they'll have access to your beautiful flowers. Nurture your long-lasting relationships, because they will come back right after Valentine's Day and buy year-round.
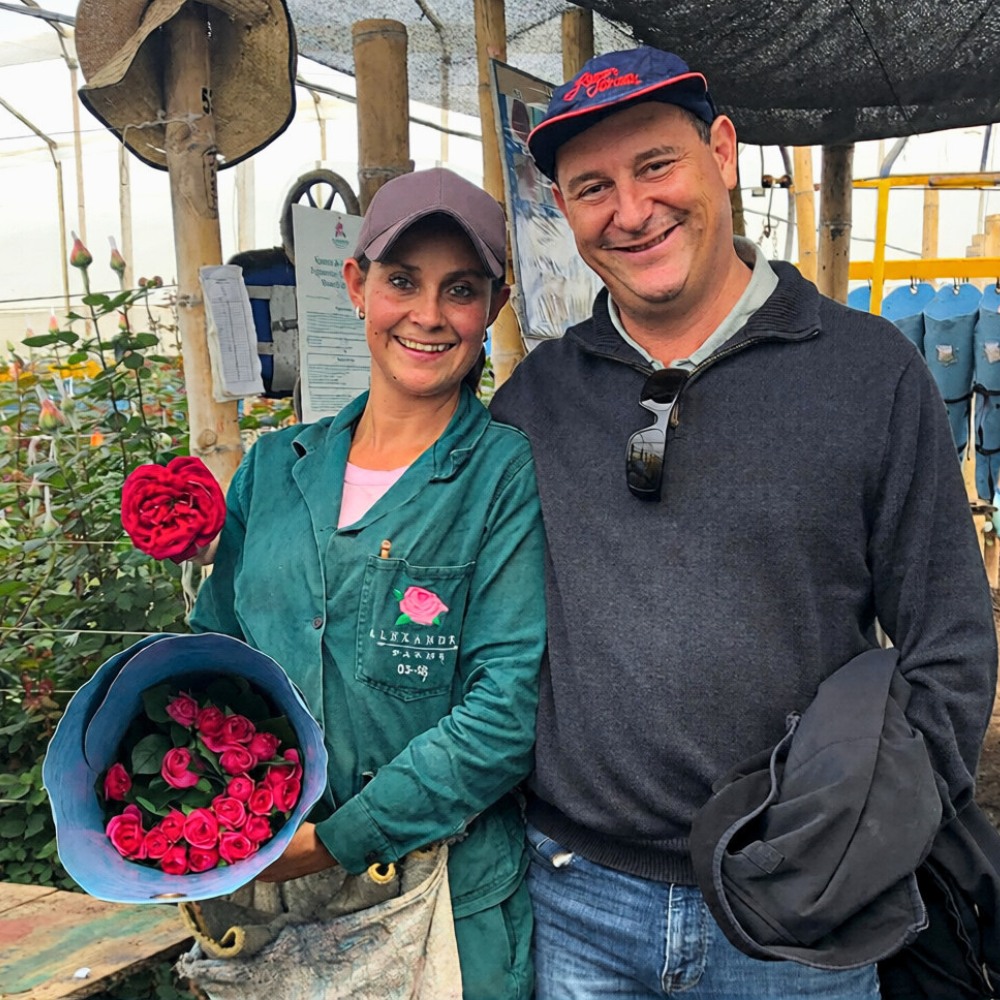

Don't underestimate the power of marketing. Leverage social media, your website, and email marketing to create anticipation and excitement around your Valentine's Day offerings. Showcase your floral arrangements with high-quality images and compelling descriptions. Build strong relationships with local wholesalers, importers, cash & carries, and florists. They are your direct link to customers and can help promote your flowers. Collaborative efforts, such as joint promotions or exclusive flower varieties, can be mutually beneficial.

4. The Transport and Cold Chain Hazard
Once the cut has been made, the Valentine's flowers begin to bloom from the end of December and reach their optimum opening point between January 15 and February 3, and are dispatched to wholesalers and auctions around the world between the last week of January. Flowers will be on the market in the week leading up to V-Day, so florists have the time to do what they're best at: creating the loveliest floral arrangements.
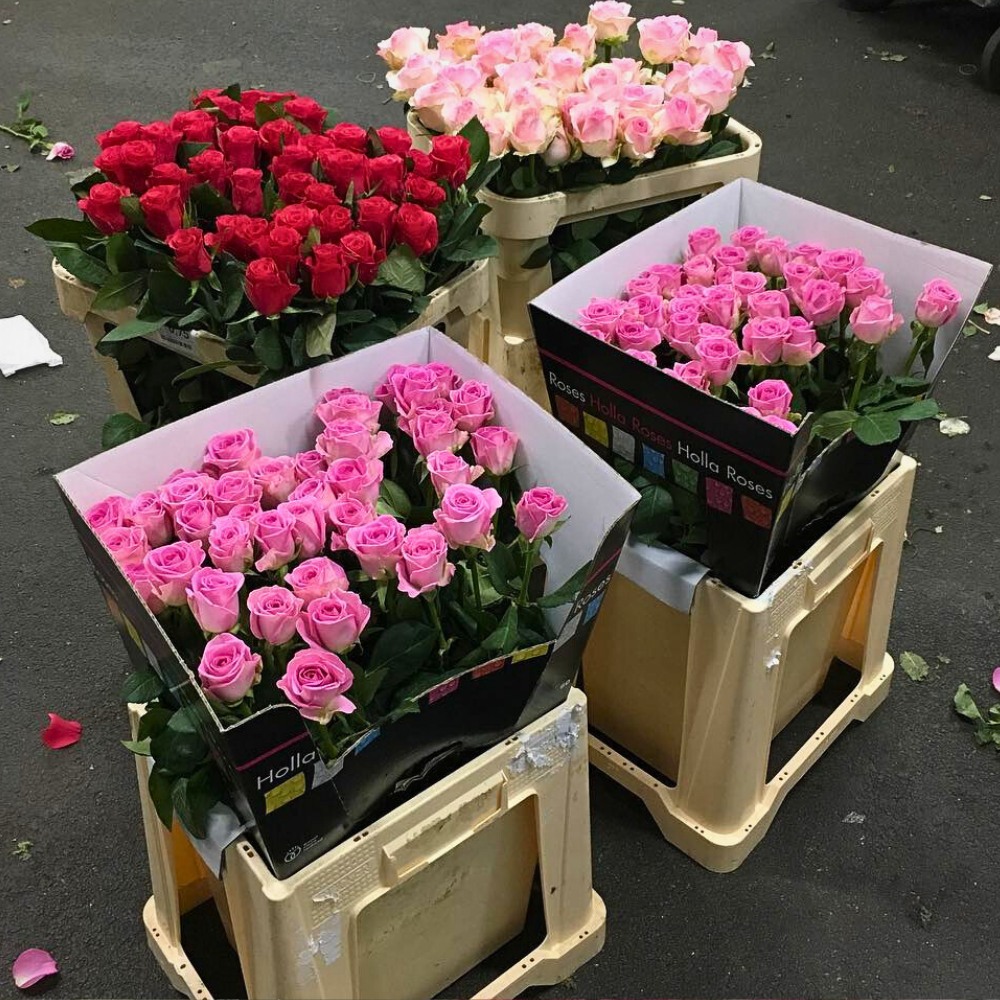

In addition to the entire production and post-harvest process, there are other factors to ensure that the flowers have the best possible durability. One of them is transport, and the other is the cold chain. For this reason, floriculturists must have adequate facilities and be able to control the entire cold chain, which ranges from when roses are in the floriculture in the cold room until they are shipped to their destination.

This process is why, in trucks where flowers are transported, the temperature must be constant around 3-5° Celsius so that the flowers do not wilt. Another fundamental aspect of transport is the humidity of the air, the same air that is measured with special sensors to guarantee the ideal humidity.

5. Offer Customization
If you have a chance, try to give a personal touch to your flowers. For large-scale operations, this must be difficult, but you could perhaps create one special and smaller, higher-valued product line that customizes your flower and/or packaging options. Valentine's Day is a time for personal expressions of love. Allow customers to customize their orders with special requests like unique bouquet arrangements or personalized messages. This personal touch can turn one-time buyers into loyal customers.
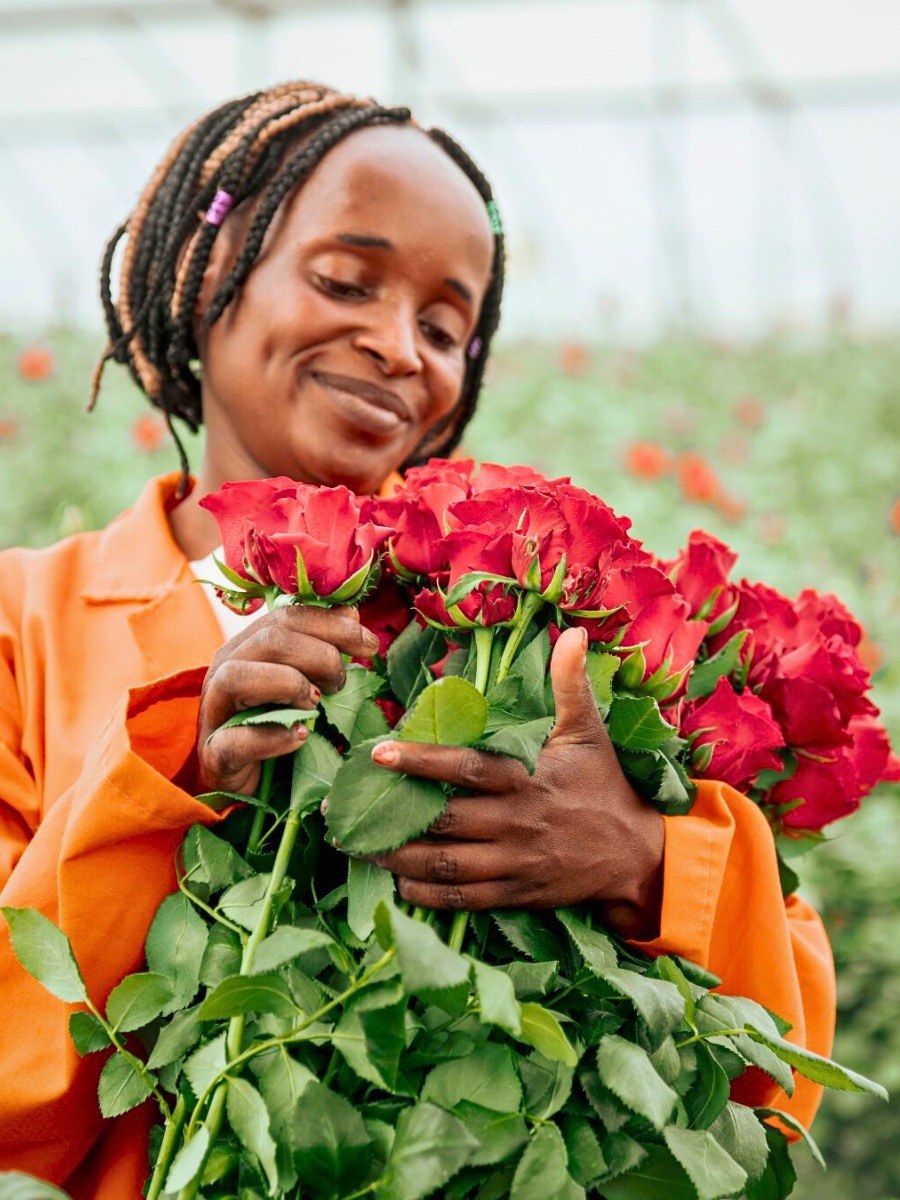

Post-Sale Customer Care
After the Valentine's Day rush, follow up with your customers to gather feedback and express your gratitude. Building positive relationships and addressing any concerns can set the stage for repeat business in the future.
In the world of flower growing, Valentine's Day is the ultimate showcase of your craft. By planning in advance, focusing on quality, and embracing creativity, you can optimize your production and sales for a successful Valentine's Day season.

Remember, it's not just about flowers; it's about helping people express their love and making their moments truly special.
For the Love of Flowers... and People
The growers play their part, just like everyone does in the floral industry. Yes, Valentine's Day is a commercial holiday in which good money is to be made. Prices can rise sky-high for this brief period.
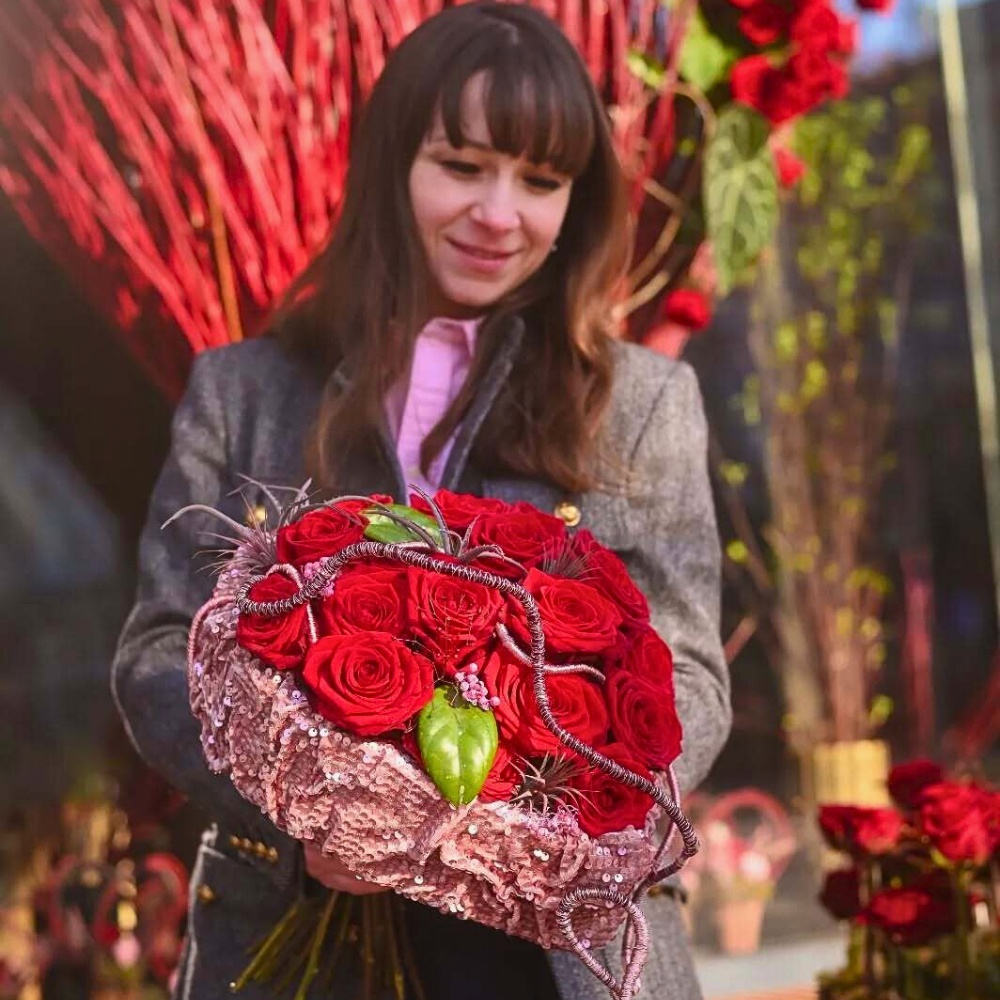

And end-customers willingly pay this, because they have only one goal: to show their love and appreciation with flowers. Growers who understand this are not in it for the money, but also for the love of flowers and people.
Feature image Rose Born Free from breeder @deruiterecuador in Ecuador.