Sustainability has become an important concept across different industries. As such, floriculture is no exception. The world today faces a myriad of environmental challenges. And as the global demand for flowers continues to rise, the floriculture industry faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices that ensure the health of ecosystems, the welfare of workers, and the economic stability of growers.
The sector is, as a result, increasingly recognizing the importance of these sustainable practices, and putting all measures in place to guarantee that they are adhered to. Essentially, sustainability in floriculture, therefore, encompasses a comprehensive approach to flower production that integrates environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic viability. Here’s what you need to know about this concept.
What is Sustainability in Floriculture?
Simply put sustainability in floriculture refers to the use of resources in a manner that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This definition, based on the ideals of the 1987 United Nations Brundtland Commission's report, puts emphasis on a balanced approach that considers environmental, economic, and social factors.
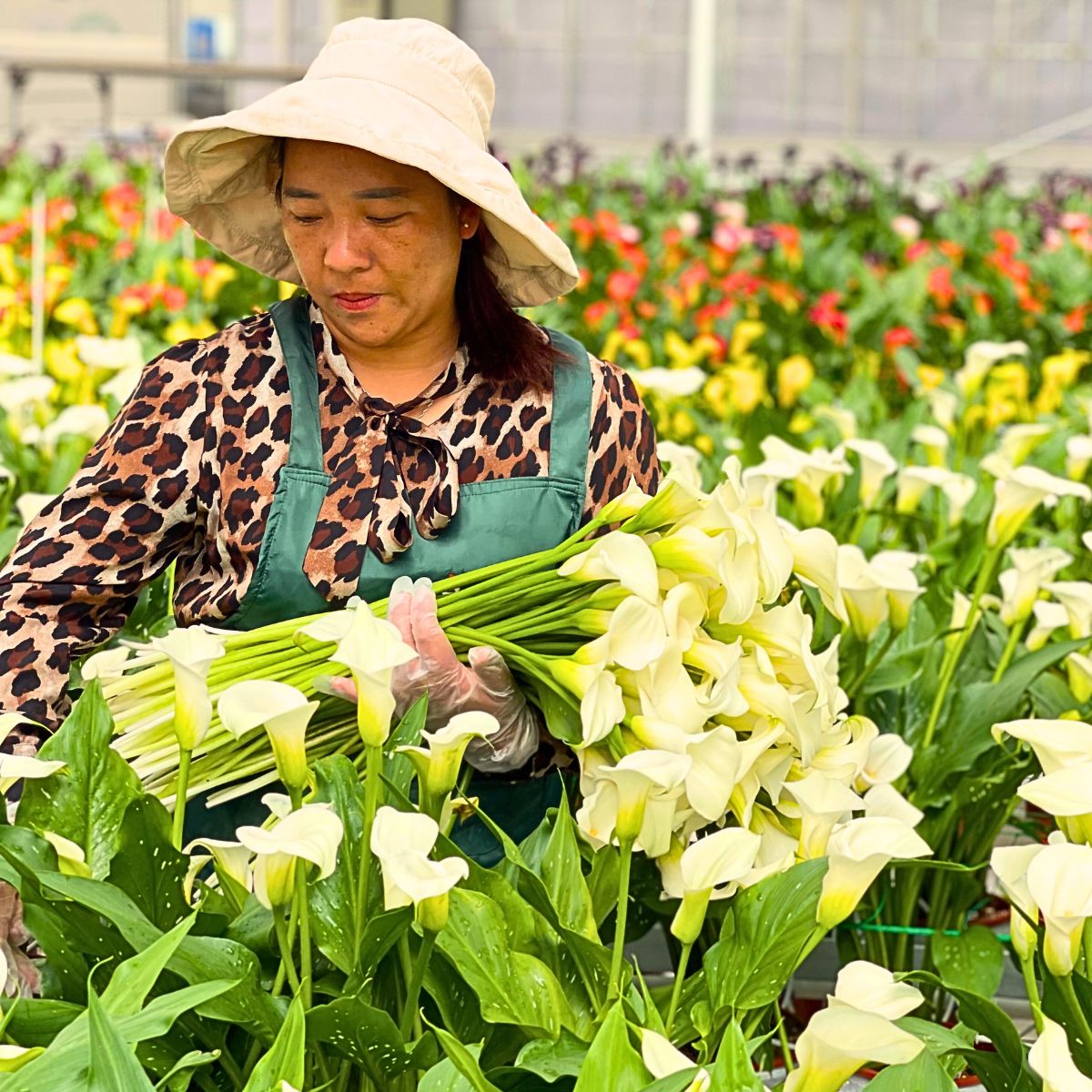

Sustainability is often defined through three interconnected pillars. These pillars are encapsulated within various sustainability certification programs such as the Floriculture Sustainability Initiative (FSI), and Florverde® Sustainable Flowers, among others which set benchmarks for growers to achieve sustainable practices across these dimensions. On the other hand, initiatives like Sustainabloom—established in 2022 by the American Floral Endowment (AFE)—provide support for the floriculture industry; guiding flower businesses through the complexities of sustainability, and providing them with research-based educational tools and resources necessary for achieving this goal.
Environmental Sustainability
This aspect focuses on minimizing the ecological footprint of flower production. It involves practices such as reducing pesticide use, conserving water, managing waste effectively, and promoting biodiversity. This puts into effect practices that protect ecosystems, conserve biodiversity, and minimize pollution. In floriculture, this can mean using organic growing methods, reducing chemical inputs, and implementing water conservation techniques. Growers are, therefore, encouraged to adopt these methods that protect natural habitats and utilize resources efficiently.

Economic Sustainability
Economic viability is crucial for the long-term success of floriculture businesses. This involves adopting practices that not only reduce costs but also enhance profitability while maintaining environmental and social standards. Sustainable economic practices may include diversifying product offerings and utilizing innovative technologies to improve efficiency. To put it in simpler terms, this pillar basically, focuses on the financial viability of floriculture businesses. Sustainable practices should not only be environmentally friendly but also economically feasible, ensuring that growers can maintain profitability while adopting greener methods.
Social Sustainability
This pillar emphasizes the importance of fair labor practices and community engagement. It incorporates safe working conditions for farm workers, providing fair wages, and supporting local communities. Social sustainability also involves transparency in supply chains and ethical sourcing of materials. This aspect of sustainability, generally, ensures the importance of social equity and community well-being in the floriculture industry. It takes account of fair labor practices, community engagement, and ensuring that the benefits of floriculture extend to all stakeholders involved.

So Why is Sustainability Essential in Floriculture?
The significance of sustainability in floriculture cannot be overstated as the flower industry continues to face challenges on different fronts. Think climate change, resource depletion, and shifting consumer preferences; the challenges are many, and hence the concept of sustainability attempts to address them to ensure favorable outcomes.
Environmental Protection
The floriculture industry has a significant impact on ecosystems due to its reliance on natural resources, ranging from pesticide use to water consumption. Sustainable practices help mitigate negative impacts such as soil degradation, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. By adopting them, the industry can reduce its ecological footprint. For instance, integrated pest management (IPM) techniques minimize chemical use, while water-efficient irrigation systems help conserve this precious resource.

Meeting Consumer Demand
Today's consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental and social implications of their purchases. There, essentially, is a growing trend among consumers who prefer sustainably sourced products, thus as awareness of environmental issues increases, customers are more inclined to choose flowers that are grown responsibly. Retailers are responding by prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate sustainable practices, making sustainability a competitive advantage for growers. Many buyers are, just the same way, willing to pay a premium for sustainably sourced flowers and plants. This shift in consumer behavior means that floriculture businesses must adapt to meet these expectations or risk losing their market share.
This, also, influences market access as many international markets require sustainability certifications as a prerequisite for trade. Thus, by adhering to sustainable practices and obtaining relevant certifications, growers can access broader markets and enhance their export opportunities.

Regulatory Compliance
Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations regarding agricultural practices, particularly concerning pesticide use and environmental impact. Floriculture businesses that adopt sustainable practices are better positioned to comply with these regulations, avoiding potential fines and penalties and enhancing their reputation.
Long-Term Viability
Sustainable practices contribute to the resilience of flower production systems by ensuring that natural resources are preserved for future generations. This approach not only protects the environment but also secures the livelihoods of those involved in floriculture. In essence, sustainability is not just a trend; it is a necessity for the long-term viability of the floriculture industry because by investing in sustainable practices, flower businesses can ensure their operations remain resilient in the face of environmental and economic challenges.
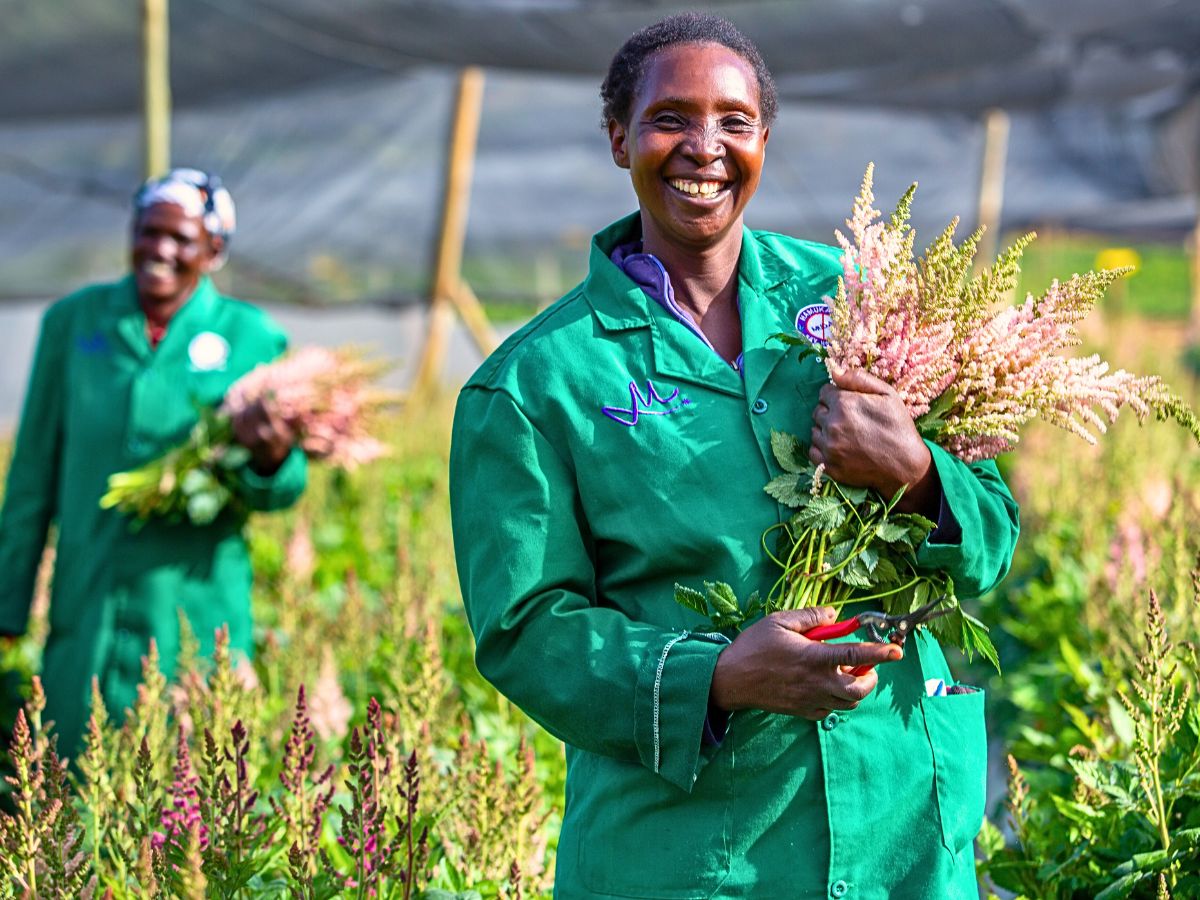

Illustrations of Sustainability in Floriculture
Several innovative initiatives exemplify how sustainability is being integrated into floriculture. All of these are geared towards the general good of the industry.
Organic Growing Practices
Perhaps one of the most visible examples of sustainability in floriculture is the adoption of organic growing practices. Organic floriculture avoids synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, relying instead on natural alternatives. This not only reduces chemical runoff into waterways but also promotes healthier ecosystems. The vast majority of flower farms across the world employ this practice in their sustainable practices.
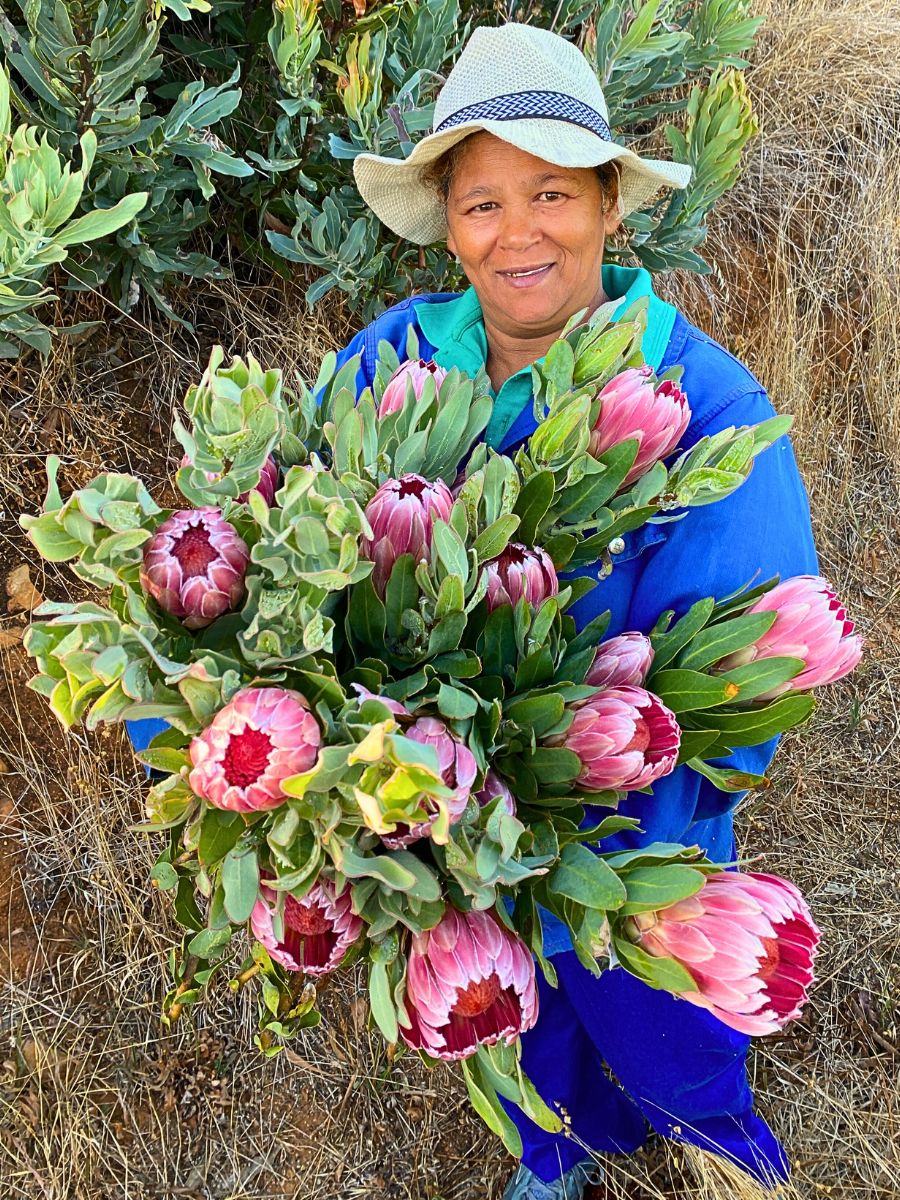

Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Growers are increasingly adopting IPM strategies that focus on biological control methods rather than chemical pesticides. For example, some farms utilize beneficial insects to control pests naturally, reducing reliance on harmful chemicals while promoting a healthier ecosystem.
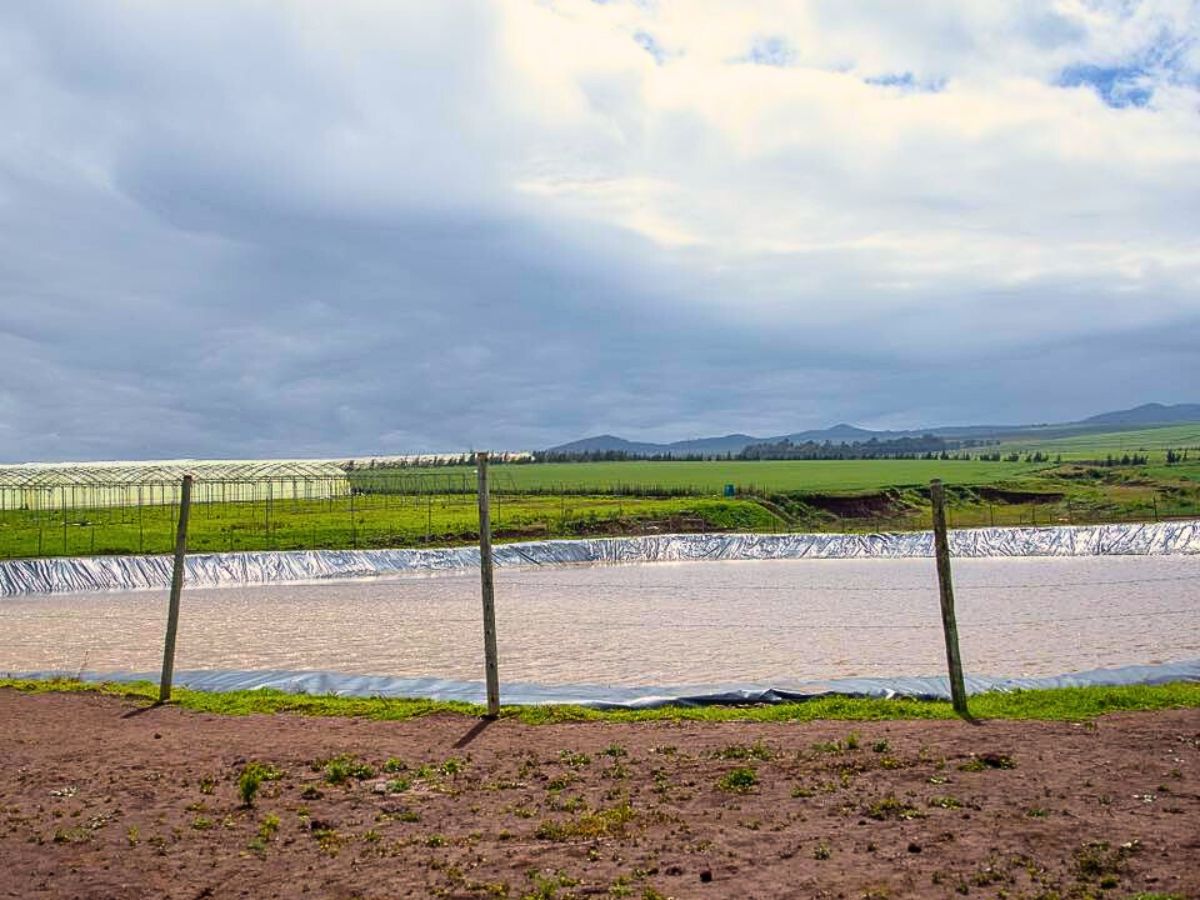
Water Conservation Techniques
Water management is critical in flower production because the scarcity of this commodity is a pressing issue in many regions. Floriculture businesses are, therefore, increasingly implementing water conservation techniques, such as drip irrigation. Additionally, rainwater harvesting systems are being employed to collect and reuse water for irrigation purposes. These methods not only reduce water usage but also lower costs for growers.
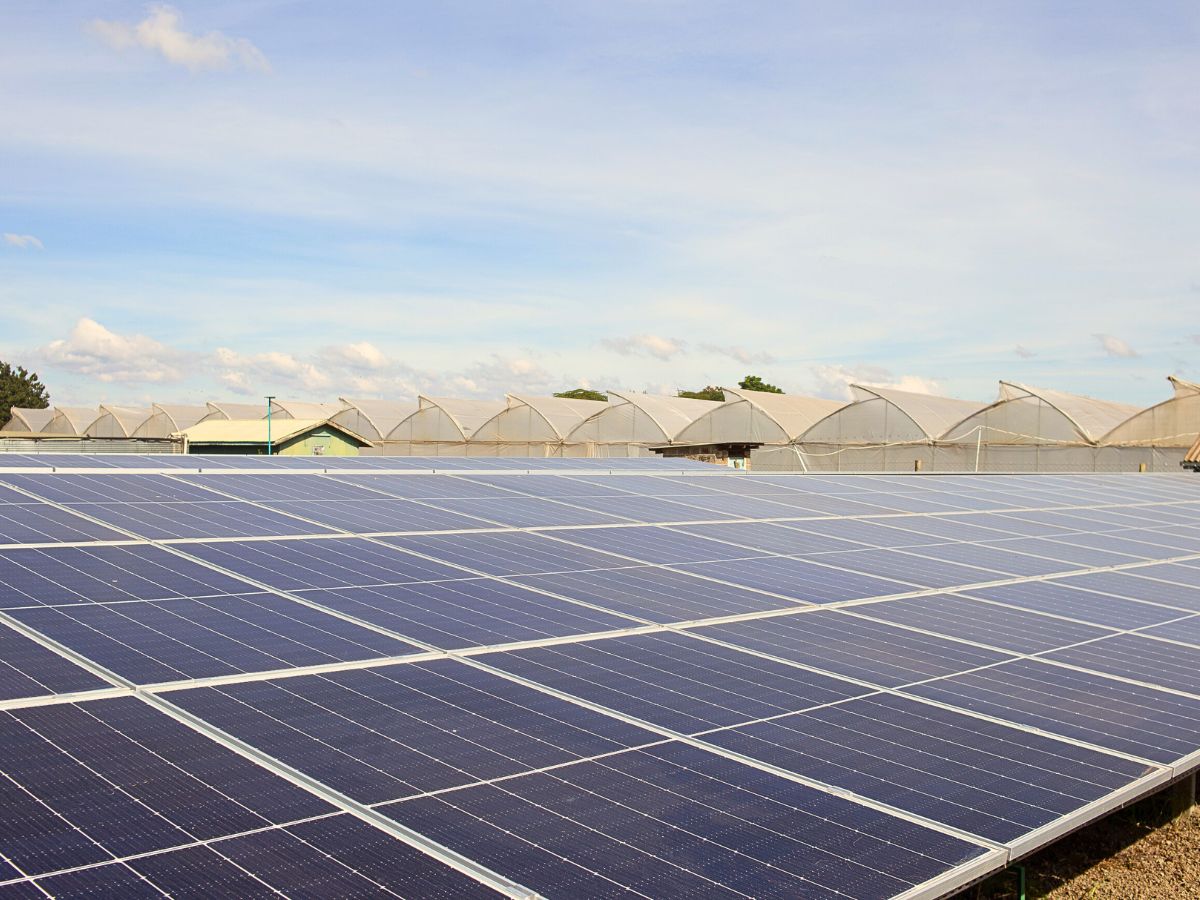


Renewable Energy Utilization
The shift towards renewable energy sources is gaining momentum in floriculture. Farms are investing in solar panels to power operations, significantly reducing their carbon footprint. There are several examples of growers turning to green energy. For instance, grower Tambuzi Roses in Kenya has achieved Carbon Neutral Gold Standard status by utilizing solar energy and engaging in community investment initiatives. The same applies to numerous other flower farms across the world.
Peat-Free Substrates
With increasing awareness about the environmental impact of peat extraction, many growers are transitioning to peat-free substrates for plant cultivation. This shift not only reduces habitat destruction but also aligns with regulatory trends aimed at conserving peatlands.

Waste Reduction Strategies and Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Many floriculture businesses are adopting waste reduction strategies, such as composting plant waste and using biodegradable packaging. These practices not only minimize landfill contributions but also create a circular economy where waste is repurposed into valuable resources. Still, in view of that, the floriculture industry is addressing packaging waste by adopting biodegradable and compostable materials instead of traditional plastic wraps. Such innovative designs that minimize packaging waste accumulation while preserving flower freshness contribute to the overall sustainability-in-floriculture cause.
Sustainable Sourcing
FSI has developed a Basket of Standards to promote responsible sourcing of flowers and plants. This initiative encourages growers to adopt environmentally and socially responsible practices, enhancing transparency and accountability in the general flower supply chain.

Fairtrade Practices and Other Standards
Fairtrade certification is another important aspect of sustainability in floriculture. This certification ensures that growers receive fair wages and work under safe conditions. Supporting Fairtrade practices guarantees that consumers can contribute to social sustainability within the industry. Across different regions, there are also other standards that flower growers adhere to, thus, enhancing sustainability in floriculture.
Community Engagement Programs
Many sustainable flower farms actively engage with local communities by supporting education initiatives or providing fair wages to workers. These programs enhance social sustainability by promoting positive relationships between growers and their communities.

Sustainability in Floriculture Is a Multifaceted Concept
Sustainability in floriculture represents a holistic approach that balances environmental health, social equity, and economic viability. As consumers increasingly demand responsibly sourced flowers, growers must adapt to meet these expectations while navigating regulatory landscapes and market dynamics. And as the industry faces increasing pressures from consumers, regulators, and environmental challenges, implementing sustainable practices becomes not just beneficial but essential for the long-term success of the flower industry.

The integration of sustainable practices not only benefits the environment but also enhances the resilience and profitability of flower production systems. Essentially, according to Sustainabloom, sustainability should be accessible to everyone in the floriculture industry. Embracing this concept in floriculture means the industry continues to thrive while contributing positively to society and preserving natural resources.
Feature image by Kapiteyn.