The global flower industry, valued at more than $60 billion and expected to grow even more is known for its beauty and economic significance. It not only supplies flowers that delight and provide enchantment but also contributes significantly to the economic viability of millions of people across the world. Yet, beneath this beauty and economic significance, lies a pressing challenge: water scarcity. The floriculture industry, which incorporates the cultivation and marketing of flowers and ornamental plants, faces significant challenges related to water use.
The heavy reliance on water—be it for irrigation, cooling, post-harvest processing, and many other relevant practices—has made the sustainable use and management of this commodity a key element of environmental and economic resilience. In consequence, as climate change heightens water scarcity in many regions, the challenge becomes a pressing global issue, and therefore sustainable water management practices are becoming quite necessary.
The Urgency of Sustainable Water Practices in Floriculture
The flower industry's thirst for water is incontestable. Flower cultivation, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions where many flower farms are located, places significant strain on local water resources. Over-extraction of groundwater can lead to depletion, land subsidence, and saltwater intrusion, rendering land unsuitable for agriculture. Furthermore, the use of inefficient irrigation techniques leads to substantial water loss through evaporation and runoff, further worsening the already dire situation.

The environmental consequences extend beyond water scarcity. The unwarranted use of fertilizers and pesticides, often associated with conventional farming practices, can contaminate water sources, harming both aquatic ecosystems and human health. The economic implications are equally significant. Water scarcity can lead to increased prices, impacting the profitability of flower farms. Furthermore, a reputation for unsustainable practices can damage a flower company's brand image, alienating environmentally conscious consumers who are increasingly demanding sustainable products. Thus, in a competitive global market, adopting sustainable water management is not merely an ethical concern; but also a crucial element of long-term economic viability.
Why Sustainable Water Use Matters in Floriculture
Sustainability is an essential subject in floriculture, particularly regarding the responsible use of water resources. And, given there are many challenges currently facing the industry, it is vital to adopt sustainable water management practices that ensure the resilience of both the industry and the ecosystems it relies on. Why, then, is sustainable water use an imperative in the floriculture industry? Well, there are several reasons for this.

Environmental Imperatives
Flower cultivation is inherently water-intensive. Growing a single rose stem can, for instance, be surprisingly water-intensive! It generally takes between seven and 13 liters of water to produce one rose stem. This includes the water used for irrigation and other related processes in the flower’s cultivation. Just so that it is clear, these flowers may be beautiful, but they do have quite a thirst! They strain local resources in water-scarce regions, especially in areas in Kenya and Ethiopia.
Extracting the commodity beyond certain levels depletes aquifers, disrupts ecosystems, and heightens competition with food crops for limited supplies. Additionally, pesticide-laden runoff from conventional farms often contaminates waterways, harming biodiversity and human health. Sustainable practices mitigate these impacts. They preserve the ecosystems for the long term.

Economic Viability
Water scarcity directly threatens profitability. Rising costs for irrigation and treatment, coupled with climate-driven droughts, squeeze margins for growers. Conversely, efficient water use reduces operational expenses. For instance, drip irrigation systems can cut water consumption by 50–75% compared to overhead methods, translating to significant savings. Sustainable practices also align with consumer demand as more than 67% of flower buyers prefer ethically sourced flowers, often tied to water management practices and certifications.
Regulatory and Market Pressures
Governments and international markets increasingly mandate sustainable water use. The European Union’s phytosanitary standards, for instance, penalize growers with poor environmental practices, while certifications like Florverde® Sustainable Flowers (FSF) and Fairtrade require adherence to sustainable floriculture practices including water conservation protocols. Non-compliance risks market exclusion. All these make sustainability a competitive necessity.

Innovations in Sustainable Water Management
Fortunately, the floriculture industry is actively exploring and implementing a range of innovative strategies to minimize its water footprint. From the vast flower farms of Colombia, Kenya, Ecuador, and Ethiopia to the tulip fields of the Netherlands and many more therein, the industry is reimagining water use through innovation, technology, and community-driven practices. These strategies cover technological advancements, improved farming practices, and a greater emphasis on water recycling and reuse.
Precision Irrigation Techniques Such as Drip Irrigation
One of the most widely adopted sustainable water management practices in the flower industry is the use of drip irrigation systems. Drip irrigation involves the slow, controlled application of water straight to the root zone of plants, reducing water waste and improving its use and efficiency. This approach has transformed water efficacy in floriculture.
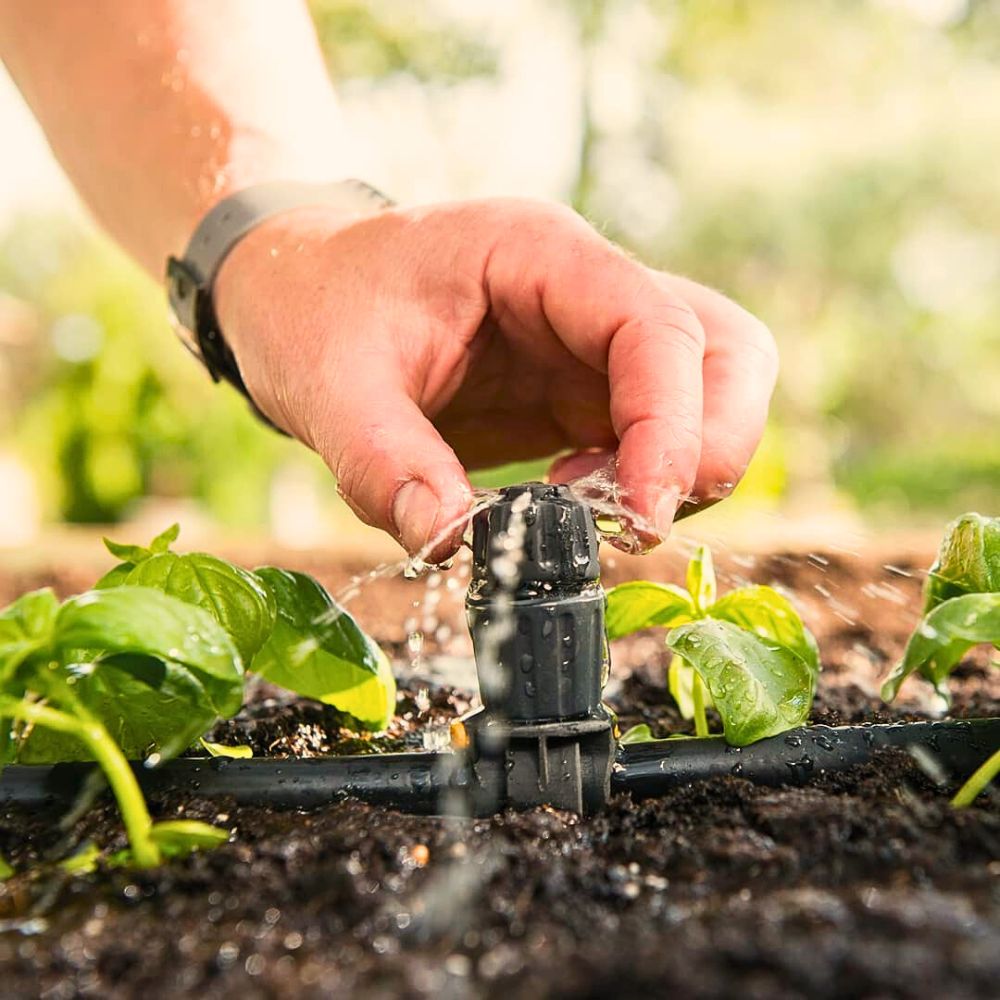

The technology which delivers water directly to plant roots through networked tubes, minimizes evaporation and runoff. In Kenya, for instance, which is one of the world's largest flower-producing countries, many flower farms have transitioned to drip irrigation systems. This has resulted in significant water savings, with some farms reporting a reduction in water usage of up to 50% compared to traditional irrigation methods. And, combined with polyethylene mulch, drip systems also suppress weeds and retain soil moisture, further conserving resources.
Kenya’s flower industry employs drip irrigation across at least 80% of its farms. This shift, supported by the Kenya Flower Council’s Flowers and Ornamentals Sustainability Standard, has helped the sector reduce its water footprint while maintaining its flower export dominance.

Rainwater Harvesting
The industry has also explored the use of alternative water sources, such as rainwater harvesting. In this case, rainwater harvesting systems collect and store precipitation for irrigation, cutting reliance on groundwater. This not only helps to reduce the industry’s dependence on conventional water sources but also contributes to the diversification of water supplies and the overall resilience of the flower production system.
Collecting rainwater from rooftops and other surfaces guarantees that flower farms can supplement their irrigation needs, reducing their overall water consumption in an approach particularly beneficial in regions with significant rainfall. The collected rainwater can be stored in reservoirs or tanks, which assures a readily available supply of water during dry periods. Several flower farms in regions with abundant rainfall have, as a result, successfully implemented rainwater harvesting systems, reducing their need for external water sources and in turn lowering their operational costs.

In Ethiopia, flower farms use rooftop catchment systems and reservoirs to offset up to 30% of their water needs. The same can be said of Kenya where growers like Sian, Kikwetu Flowers, Red Lands Roses, and Tambuzi, among a host of many others, exemplify this approach, integrating rainwater harvesting with solar-powered pumps to achieve carbon-neutral status. In Colombia, according to Daniela España, the director of FSF, up to 60% of the water used in the country’s flower production comes from rainwater harvesting, which significantly reduces the dependency on surface and groundwater resources.
Daniela España:
“100% of Colombian flower farms have rainwater collection systems making the industry in the country a global pioneer in sustainable water management. 95% of the farms use drip irrigation. And, the different Florverde-certified farms have implemented a closed water cycle system minimizing waste and optimizing the resource’s use.”

Water-Efficient Greenhouse Technologies
Modern greenhouses equipped with different technological innovations including hydroponics, closed-loop systems, climate control systems, and energy-efficient technologies, likewise, significantly reduce water in different ways. These systems allow for enhanced water management, and precise control of temperature, humidity, and ventilation, which creates an optimal growing environment that minimizes water stress on plants.
Soil-free hydroponic systems, also, allow growers to cultivate their flowers in nutrient-rich solutions, slashing water by a huge percentage. Closed-loop systems, on the other hand, recycle drainage water, minimizing waste.

Wastewater Recycling and Treatment
Another sustainable water management strategy employed by the flower industry is water recycling and reuse. Treating and reusing water from various stages of the flower production process enables growers to reduce their overall water consumption and minimize their environmental impact, as generally, water recycling and reuse represent a significant step towards minimizing the industry's water footprint.
Treated wastewater from greenhouses or other sources can be reused for irrigation, significantly reducing the demand for freshwater resources. However, this approach requires careful planning and implementation to ensure that the recycled water is free from harmful contaminants that could affect plant health or soil quality.

Many flower growers are investing in wastewater treatment facilities to enable water reuse; a key component of circular economy principles. For instance, several Dutch flower growers are pioneers in water recycling, employing advanced treatment systems to purify wastewater for reuse in their greenhouses. Advanced treatment systems are increasingly central to managing wastewater effectively. Solutions like MBBR Media Direct offer expert MBBR carriers and specialized media that enhance the efficiency and reliability of water recycling within horticultural operations, supporting sustainable practices by improving both quality and resource usage. This practice not only conserves water but also reduces the environmental impact associated with wastewater discharge.
These growers' water treatment systems allow them to recycle and reuse up to 90% of the water used in their operations, which not only reduces their water footprint but also helps to mitigate the risk of water pollution; ensuring that any wastewater is appropriately treated before being released into the environment. Advanced treatment technologies, further, enable farms to reuse graywater (from cleaning and cooling), repurposing it for greenhouse irrigation. Moreover, several Kenyan farms use constructed wetlands to filter and recycle water, reducing this resource’s depletion.

Improved Soil Management, and Integrated Water Management Practices
Effective soil management practices, also, play an essential role in optimizing water use. Practices such as mulching and the addition of organic matter can enhance soil structure and water retention, reducing the frequency and volume of irrigation required. Many flower farms are adopting soil health management practices, including cover cropping and reduced tillage, to improve water retention and lessen water stress on plants.
The industry is, furthermore, increasingly acknowledging the importance of adopting an all-inclusive integrated approach to water management. This includes implementing comprehensive water management plans, adopting best management practices, and building collaboration between growers, policymakers, and other stakeholders to ensure the long-term sustainability of water usage.
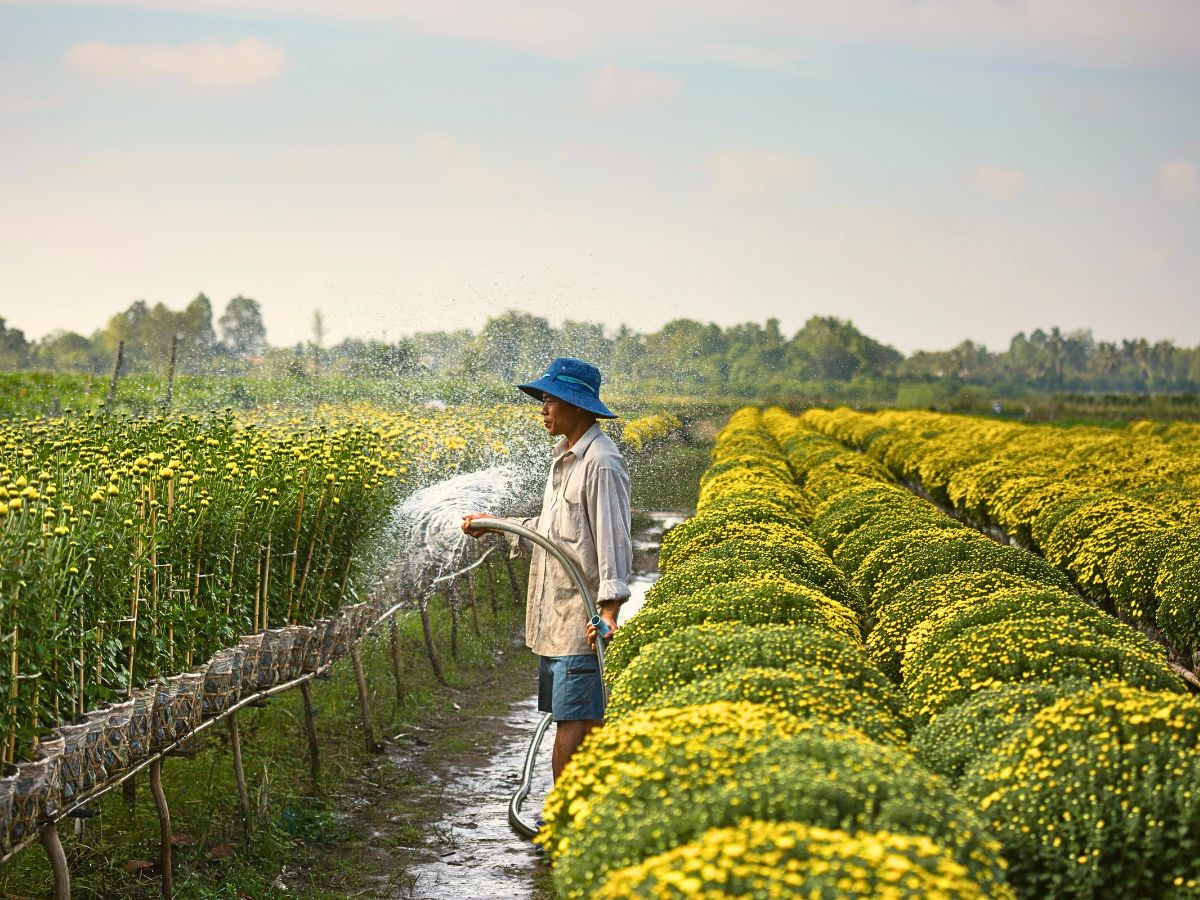

Climate-Smart Floriculture
Climate-smart approaches such as the adoption of drought-resistant cultivars and soil moisture sensors that optimize water use are, also, vital. In countries like Colombia, Kenya, and numerous others, growers employ the use of satellite-based systems to guide some essentials like irrigation scheduling to align watering with real-time weather data. This significantly cuts water usage.
Breeding and cultivating drought-tolerant flower varieties is, also, a long-term strategy that could address the root cause of high water consumption. Selecting and developing varieties that require less water could guarantee that the industry significantly reduces its overall water footprint. This approach, however, requires collaboration between researchers, breeders, and growers to identify and propagate suitable varieties adapted to specific climatic conditions.

The Role of Certification and Regulation in Sustainable Water Use
To further promote sustainable water use in the flower industry, numerous certification and regulatory frameworks have been developed, all of which set standards and guidelines for the industry, that ensure growers and producers are held accountable for their water usage and consequent environmental impact.
Certification programs like the Rainforest Alliance Certified™ standard, for instance, require flower growers to meet stringent criteria related to water conservation, pollution prevention, and the protection of water resources. Growers who achieve this certification demonstrate their obligation to sustainable practices, more so water management, and can use the certified seal to differentiate their products in the market.

In addition, many countries have also implemented regulatory frameworks to govern their flower industries’ water usage. For example, in the European Union, the Water Framework Directive sets out a comprehensive approach to water management, requiring members to develop and implement management plans that address the sustainable use of water resources, including in the farming sector.
Similarly, in some countries, national regulations and policies have been put in place to regulate the water usage of the flower industry, with a focus on water allocation, pollution control, and the protection of water-related ecosystems. These certification and regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in driving the adoption of sustainable water management practices in the flower industry; growers and producers are required to validate their compliance with environmental standards and regulations to remain competitive in the global flower market.

What Is the Future of Sustainable Water Use in the Flower Industry?
To meet the ever-evolving market demands and ensure the long-term viability of the floriculture industry, flower growers and producers need to continue investing in innovative water management innovations, implement comprehensive water management plans, and work with policymakers and other stakeholders to develop and implement effective water governance frameworks.
Additionally, the industry needs to explore new and emerging strategies for water conservation, such as the use of drought-resistant plant and flower varieties, the implementation of precision systems that use real-time data and machine learning, and the enhancement of renewable energy sources to power water pumping and treatment systems.

In all that, what is important to note is that embracing a more sustainable and responsible approach to water use in the floriculture industry means the industry not only reduces its environmental footprint but also positions itself as vital in the global efforts to ensure the long-term availability and quality of this precious resource. Taking responsibility for sustainable water management is an important factor in the flower industry’s success as well as the well-being of the communities and ecosystems it serves.
Feature image by Decorum., header image by רפאל Pikiwiki Israel.